Archiv für die 'Blog' Kategorie


Einführung
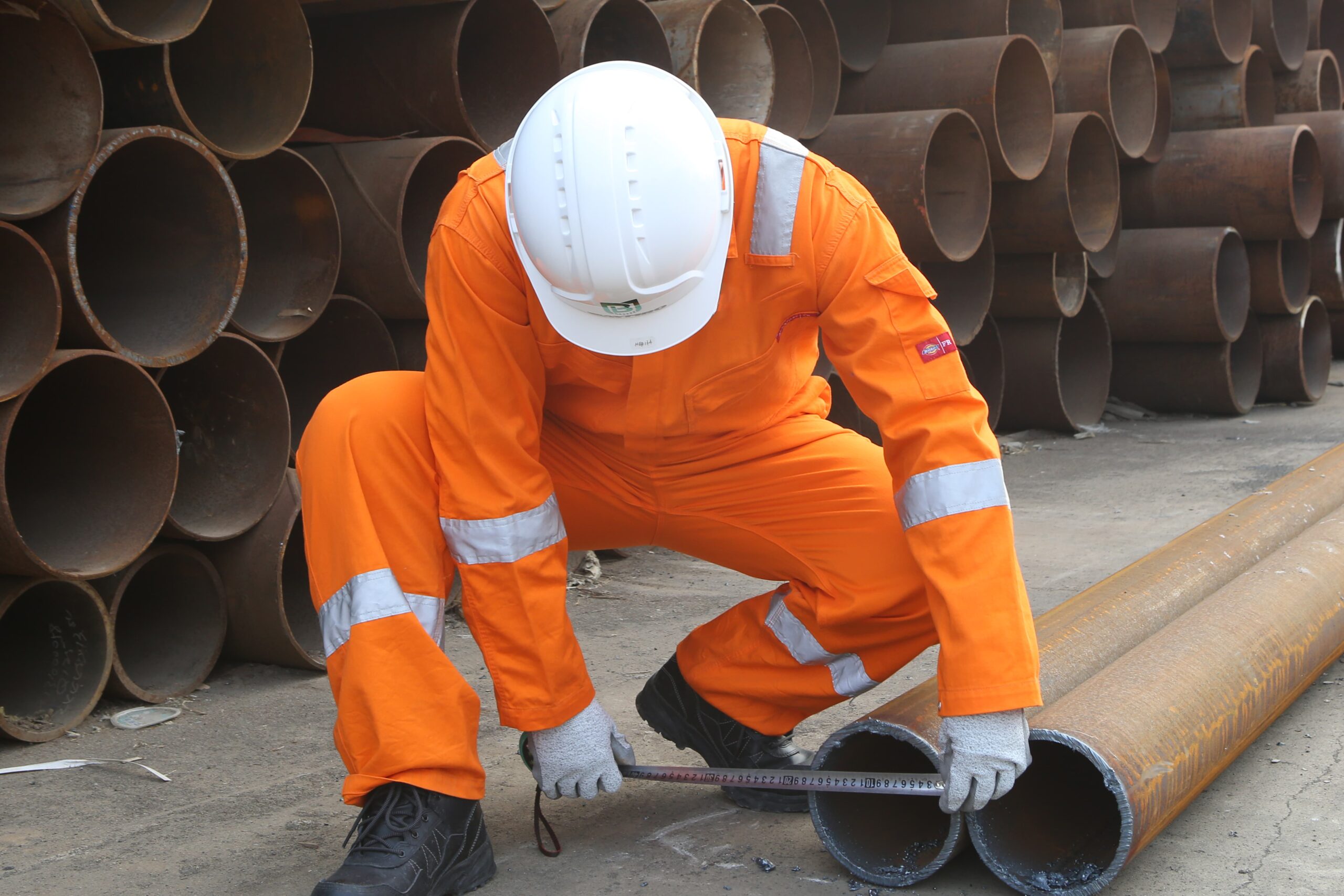
Personal Protective Equipment, commonly known as PPE, is a vital component of workplace safety across various industries and has taken on newfound importance in our daily lives during the COVID-19 pandemic. PPE serves as a shield, safeguarding individuals from a range of potential hazards, ensuring their well-being, and enabling them to perform their tasks effectively. In this article, we will delve into the world of PPE, discussing what it is, its classifications, common usage scenarios, and how to choose the right PPE for specific situations.
What is PPE?
Personal Protective Equipment, or PPE, refers to specialized gear, equipment, or clothing designed to protect individuals from workplace or environmental hazards that could cause injury, illness, or even death. PPE acts as a barrier between the wearer and various risks, including physical, chemical, biological, radiological, and electrical dangers.
Classifications of PPE
PPE can be classified into several categories, each tailored to address specific types of hazards. The primary classifications include:
Kopfschutz: This category includes safety helmets or hard hats, which shield the head from falling objects, electrical shocks, and impacts. They are commonly used in construction and industrial settings.
Schutz für Augen und Gesicht: Safety glasses, goggles, and face shields protect the eyes and face from flying debris, chemicals, intense light, and splashes. These are essential in industries like welding, woodworking, and laboratories.
Gehörschutz: Earplugs and earmuffs are used to reduce exposure to high noise levels, preventing hearing loss in noisy work environments, such as manufacturing plants or construction sites.
Schutz der Atemwege: Respirators, including N95 masks and full-face respirators, filter out harmful particles and contaminants from the air. They are critical in healthcare, construction, and industries dealing with airborne hazards.
Schutz für Hände und Arme: Gloves, sleeves, and gauntlets are used to protect hands and arms from cuts, chemical exposure, burns, and abrasions. Workers in healthcare, manufacturing, and laboratories frequently use these.
Körperschutz: This category includes coveralls, aprons, and vests, designed to safeguard the torso and limbs from chemical, biological, radiological, or physical hazards. Industries such as healthcare, hazardous material handling, and agriculture employ body protection.
Foot and Leg Protection: Safety boots or shoes with reinforced toes and slip-resistant soles protect the feet from falling objects, punctures, electrical hazards, and slips. They are indispensable in construction, manufacturing, and mining.
Absturzsicherung: Harnesses, lanyards, and lifelines are essential for preventing falls from heights and are commonly used in construction, maintenance, and roofing.
Scenarios of PPE Usage
PPE finds application in a wide range of scenarios:
Healthcare: Healthcare workers use PPE such as masks, gloves, gowns, and face shields to protect themselves and patients from infections and other hazards.
Construction: Construction workers rely on PPE like hard hats, safety vests, gloves, and fall protection equipment to mitigate the risks of falling objects, slips, trips, and falls.
Chemical Handling: Workers handling chemicals use PPE like chemical-resistant suits, gloves, and goggles to prevent exposure to corrosive or toxic substances.
Welding: Welders wear helmets with face shields, welding gloves, and flame-resistant clothing to shield themselves from intense heat and UV radiation.
Manufacturing: Employees in manufacturing industries use PPE like safety glasses, hearing protection, and protective clothing to stay safe from various workplace hazards.
How to Choose PPE
Selecting the right PPE is crucial for safety. Here are some steps to guide you in making the correct choices:
Identify Hazards: Conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify potential hazards in your work environment.
Understand Regulations: Familiarize yourself with local and national regulations and standards governing PPE use in your industry.
Select Appropriate PPE: Choose PPE that is specifically designed to protect against the identified hazards. Ensure it fits properly and is comfortable to wear for extended periods.
Training and Education: Train employees on the proper use, maintenance, and limitations of PPE. Make sure they understand when and how to use it.
Regular Maintenance: Inspect and maintain PPE regularly to ensure it remains effective. Replace damaged or worn-out equipment promptly.
Evaluate and Adjust: Continuously evaluate your PPE program and make necessary adjustments based on feedback and changing workplace conditions.
Schlussfolgerung
Remember that your safety should always be a top priority. Properly selected and maintained PPE plays a crucial role in reducing the risks associated with various workplace hazards.
GB 14866-2006 is a Chinese national standard that sets forth the specifications and requirements for safety glasses. Developed by the Standardization Administration of China (SAC), this standard is crucial for ensuring the safety of individuals who use protective eyewear in various industrial and occupational settings within China. Here’s an overview of GB 14866-2006:

1. Zweck und Umfang
GB 14866-2006 primarily focuses on safety glasses used to protect the eyes from various hazards, including mechanical impacts, chemical splashes, dust, and optical radiation. The standard aims to establish a consistent framework for the design, testing, and performance of these protective glasses.
2. Arten von Schutz
This standard covers a range of protective eyewear, including safety glasses, goggles, and face shields. These devices are designed to safeguard the eyes against different risks commonly encountered in industrial, construction, laboratory, and other work environments.
3. Anforderungen an die Gestaltung
GB 14866-2006 outlines design requirements for safety glasses, ensuring they provide comprehensive protection without compromising comfort and usability. These requirements encompass factors such as impact resistance, optical clarity, and frame construction.
4. Prüfverfahren
Safety glasses that comply with GB 14866-2006 must undergo rigorous testing procedures to verify their compliance with the standard. These tests evaluate various aspects of performance, including impact resistance, optical quality, and resistance to environmental factors.
5. Kennzeichnung und Beschriftung
Products that meet the GB 14866-2006 standard must be marked and labeled accordingly. These markings typically include information about the manufacturer, product model, and compliance with the standard. Such markings help users identify suitable eyewear for their specific needs.
6. Sicherheit am Arbeitsplatz
Compliance with GB 14866-2006 is essential for maintaining workplace safety in China. Employers are often required to provide and enforce the use of GB-compliant protective eyewear to reduce the risk of eye injuries in hazardous work environments.
7. Kompatibilität
GB 14866-2006 is often compatible with other Chinese workplace safety standards, allowing for a comprehensive approach to employee protection. This compatibility ensures that various aspects of safety gear, such as head protection or respiratory protection, can work together effectively.
In summary, GB 14866-2006 is a crucial Chinese national standard that sets the requirements for safety glasses and protective eyewear used in a variety of work environments. Compliance with this standard helps mitigate the risk of eye injuries and promotes a safer and healthier workplace in China. Users and employers should ensure that the eyewear they use meets GB 14866-2006 standards to enhance safety and reduce the risk of accidents and injuries in the workplace.


ANSI Z87.1 ist eine wichtige Norm, die vom American National Standards Institute (ANSI) entwickelt wurde, um die Sicherheit und den Schutz von Industriearbeitern vor verschiedenen Gefahren zu gewährleisten, die die Augen und das Gesicht betreffen können. Diese Norm befasst sich speziell mit Augen- und Gesichtsschutzprodukten wie Schutzbrillen, Gesichtsschutzschildern, Schweißerhelmen und mehr. Wir wollen aufschlüsseln, was ANSI Z87.1 und seine Bedeutung:
1. Zweck der ANSI Z87.1
ANSI Z87.1 dient als umfassender Satz von Richtlinien und Anforderungen zum Schutz der Augen und des Gesichts von Arbeitnehmern in industriellen und beruflichen Umgebungen. Die Norm soll die Sicherheit am Arbeitsplatz erhöhen, indem sie strenge Kriterien für die Gestaltung, Prüfung und Leistung von Schutzbrillen und Gesichtsschutzschilden festlegt.
2. Abgedeckte Arten von Schutz
ANSI Z87.1 umfasst eine breite Palette von Augen- und Gesichtsschutzprodukten, darunter:
Schutzbrillen: Schutzbrillen, die die Augen vor verschiedenen Gefahren schützen, z. B. vor Stößen, Chemikalien und UV-Strahlung.
Schutzbrille: Schutzbrillen bieten eine umfassendere Abdichtung um die Augen und schützen vor Spritzern, Staub und chemischen Gefahren.
Gesichtsschutzschilder: Diese Schutzvorrichtungen bedecken das gesamte Gesicht und bieten zusätzlichen Schutz vor Stößen, Chemikalienspritzern und anderen Gefahren. Sie werden oft in Verbindung mit anderen Schutzbrillen verwendet.
Schweißerhelme: Helme, die für Schweißanwendungen entwickelt wurden und Schutz vor intensivem Licht, Hitze und umherfliegenden Trümmern bieten.
3. Anforderungen an die Gestaltung
In der Norm werden Designanforderungen für Augen- und Gesichtsschutzprodukte festgelegt. Diese Anforderungen umfassen Spezifikationen für Stoßfestigkeit, optische Klarheit und Rahmenkonstruktion. Die Stoßfestigkeit stellt sicher, dass die Schutzausrüstung eine bestimmte Kraft aushalten kann, ohne zu brechen oder zu zersplittern, und somit einen wirksamen Schutz im Falle eines Aufpralls bietet.
4. Prüfanforderungen
ANSI Z87.1 umfasst strenge Prüfanforderungen, denen sich die Produkte unterziehen müssen, um ihre Übereinstimmung mit der Norm nachzuweisen. Bei diesen Tests werden verschiedene Leistungsaspekte wie Stoßfestigkeit, optische Qualität und Beständigkeit gegen Umwelteinflüsse bewertet.
5. Kennzeichnung und Beschriftung
Produkte, die den Anforderungen der ANSI Z87.1 müssen entsprechend gekennzeichnet und etikettiert sein. Diese Kennzeichnungen geben das angebotene Schutzniveau an und liefern wichtige Informationen über den Hersteller und die Konformität des Produkts.
6. Sicherheit am Arbeitsplatz
Die Annahme von ANSI Z87.1 konformen Augen- und Gesichtsschutzprodukten am Arbeitsplatz trägt zur Sicherheit und zum Wohlbefinden der Industriearbeiter bei. Sie verringern das Risiko von Augenverletzungen durch mechanische, chemische und andere Gefahren und sind damit ein wesentlicher Bestandteil von Programmen zur Sicherheit am Arbeitsplatz.
Zusammengefasst, ANSI Z87.1 ist eine wichtige amerikanische Norm, die Maßstäbe für die Gestaltung, Prüfung und Leistung von Augen- und Gesichtsschutzausrüstungen setzt, die in der Industrie und am Arbeitsplatz verwendet werden. Die Einhaltung dieser Norm ist für Arbeitgeber und Einzelpersonen unerlässlich, um sicherzustellen, dass Schutzbrillen und Gesichtsschutzschilde die mit verschiedenen Gefahren am Arbeitsplatz verbundenen Risiken wirksam mindern und so eine sicherere Arbeitsumgebung fördern.

EN 1731 is a European standard that specifies the requirements for face shields designed to protect against various hazards, particularly mechanical ones. These face shields are essential safety equipment, providing reliable protection for the eyes and face. In this article, we’ll explore the key aspects of EN 1731 and understand its significance in ensuring safety in professional and industrial settings.
1. Material Specifications
EN 1731 outlines material specifications, ensuring that face mesh protectors are constructed from materials that can withstand mechanical hazards. These materials are chosen for their durability and ability to provide effective protection against impacts, flying debris, and other potential dangers.
2. Design Requirements
The standard also defines design requirements for face shields, ensuring that they provide adequate coverage for the eyes and face. Proper design is crucial to ensure that the protector offers comprehensive protection without hindering the wearer’s vision or comfort.
3. Performance Standards
EN 1731 sets performance standards for face mesh protectors, specifying the level of protection they should provide. This includes protection against impacts, such as those caused by flying objects, projectiles, or other mechanical hazards. Meeting these performance standards is essential to ensure that the protector effectively safeguards the wearer.
4. Test Methods
The standard includes detailed test methods that manufacturers must follow to assess the performance of their face mesh protectors. These tests help ensure that the protectors meet the required safety standards. Common tests may include impact resistance tests and tests for the integrity of the mesh material.
5. Reliable Protection
Face mesh protectors that conform to EN 1731 are known for their reliability in protecting against mechanical hazards. They are particularly suitable for professional use in industrial and work environments where the risk of flying debris or other mechanical dangers is high.
6. Industrial Applications
EN 1731 compliant face shields are commonly used in various professional and industrial applications, including construction, manufacturing, forestry, and agriculture. They provide essential protection for workers exposed to potential hazards, reducing the risk of eye and face injuries.
7. User Comfort
Sicherheit ist zwar oberstes Gebot, EN 1731 also considers user comfort. Properly designed face shields are comfortable to wear for extended periods, ensuring that workers can perform their tasks effectively without discomfort.
Zusammengefasst, EN 1731 is a crucial European standard that sets the requirements for face mesh protectors used in professional and industrial settings. These protectors are essential for safeguarding the eyes and face against mechanical hazards, making them a vital part of personal protective equipment. Choosing EN 1731 compliant face shields ensures that workers are adequately protected in environments where mechanical dangers are prevalent, promoting safety and reducing the risk of injuries.


EN 379 ist eine europäische Norm, die die Spezifikationen und Prüfverfahren für Automatikschweißfilter für den persönlichen Augenschutz festlegt. Diese Spezialfilter sind so konzipiert, dass sie ihre Lichtdurchlässigkeit automatisch anpassen, um optimalen Schutz zu bieten, wenn ein Schweißlichtbogen gezündet wird. Diese Norm ist entscheidend für die Sicherheit und den Komfort der Schweißer, da sie die Leistung dieser dynamischen Filter regelt. Im Folgenden werden die wichtigsten Merkmale und die Bedeutung von DE 379:
https://baymrosafety.com/product-category/face-protection/
1. Ressourcenfilter mit veränderbaren Skalennummern
DE 379 umfasst zwei Arten von automatischen Schweißfiltern. Der erste Typ, der als "Ressourcenfilter mit veränderbarer Skalennummer" bezeichnet wird, ermöglicht es dem Benutzer, die Skalennummer des Filters manuell einzustellen, um den gewünschten Grad der Lichtdurchlässigkeit beim Schweißen zu erreichen. Diese Flexibilität ist wertvoll, da verschiedene Schweißverfahren und -bedingungen unterschiedliche Schutzgrade erfordern können.
2. Quellenfilter mit automatischer Skalenzahlanpassung
Die zweite Art von automatischen Schweißfiltern, die von DE 379 wird als "Strahlenschutzfilter mit automatischer Skalenzahlanpassung" bezeichnet. Diese Filter sind besonders innovativ, da sie ihre Lichtdurchlässigkeit automatisch an die Intensität des Schweißlichtbogens anpassen. Wenn der Lichtbogen gezündet wird, verdunkelt sich der Filter schnell, um die Augen des Schweißers vor dem intensiven Licht und der Strahlung zu schützen. Nach dem Erlöschen des Lichtbogens wird der Filter wieder heller, um eine bessere Sicht zu gewährleisten. Durch diese dynamische Anpassung wird sichergestellt, dass Schweißer den notwendigen Schutz haben, ohne ihre Sicht bei der Arbeit zu beeinträchtigen.
3. Kontinuierliche Überwachung und Zündzeitpunkt
DE 379 ist in den Fällen von Bedeutung, in denen automatische Schweißfilter zur kontinuierlichen Überwachung des Schweißprozesses und nur während der Zündzeit des Lichtbogens eingesetzt werden. In solchen Fällen stellen die Anforderungen der Norm sicher, dass die Filter die erforderlichen Sicherheits- und Leistungskriterien erfüllen, damit die Schweißer effektiv und sicher arbeiten können.
4. Einhaltung und Prüfung
Die Hersteller von automatischen Schweißfiltern müssen Folgendes einhalten DE 379 Standards und unterziehen ihre Produkte strengen Tests. Durch diese Prüfungen wird sichergestellt, dass die Filter die festgelegten Anforderungen an Leistung, Haltbarkeit und Sicherheit erfüllen. Die Einhaltung der EN 379 gibt den Anwendern die Gewissheit, dass ihre Augenschutzausrüstung einen zuverlässigen und beständigen Schutz bietet.
5. Türkisches Normungsinstitut (TSE)
Das Türkische Normungsinstitut (TSE) hat folgende Normen verabschiedet und veröffentlicht DE 379 als nationale Norm in der Türkei. Das bedeutet, dass die Hersteller und Anwender von automatischen Schweißfiltern in der Türkei die Anforderungen der DE 379 um die Sicherheit und Wirksamkeit dieser Filter zu gewährleisten.
Zusammengefasst, DE 379 ist eine wichtige europäische Norm, die die Leistung und Sicherheit von automatischen Schweißfiltern für den persönlichen Augenschutz regelt. Diese Filter, ob Ressourcenfilter mit veränderbaren Skalennummern oder Quellenfilter mit automatischer Skalennummernanpassung, sind unerlässlich, um die Augen der Schweißer vor dem intensiven Licht und der Strahlung zu schützen, die bei Schweißprozessen entstehen. Einhaltung von DE 379 Normen ist wichtig, um sicherzustellen, dass diese Filter einen zuverlässigen und anpassungsfähigen Schutz für Arbeitnehmer in Schweißumgebungen bieten.
EN 175: Persönliche Schutzausrüstung für Augen- und Gesichtsschutz beim Schweißen und verwandten Verfahren
2023

EN 175 ist eine europäische Norm, die Sicherheitsanforderungen und Prüfverfahren für persönliche Schutzausrüstungen (PSA) zum Schutz der Augen und des Gesichts von Arbeitnehmern bei Schweiß-, Schneid- und ähnlichen Arbeiten festlegt. Diese Norm ist von entscheidender Bedeutung für die Gewährleistung der Sicherheit von Personen, die den verschiedenen mit diesen industriellen Prozessen verbundenen Gefahren ausgesetzt sind. Lassen Sie uns die wichtigsten Aspekte der DE 175:
1. Schutz vor optischer Strahlung und spezifischen Gefährdungen
DE 175 konzentriert sich in erster Linie auf PSA, die vor schädlicher optischer Strahlung schützen, wie z. B. vor dem intensiven Licht und der Strahlung, die bei Schweiß- und Schneidarbeiten entstehen. Sie befasst sich auch mit anderen spezifischen Risiken und Gefahren, die mit diesen Prozessen verbunden sind, darunter ergonomische, feuerbedingte, mechanische und elektrische Risiken.
2. Einbindung von Schutzfiltern
Die Norm schreibt vor, dass die entsprechende PSA mit Schutzfiltern ausgestattet sein muss, entweder mit oder ohne Abdeck-/Hintergrundokularen. Diese Filter sind entscheidend für den Schutz der Augen und des Gesichts vor dem intensiven Licht und der Strahlung, die beim Schweißen und ähnlichen Arbeiten entstehen. Die Verwendung dieser Filter wird vom Hersteller des Schweißerschutzes empfohlen und muss der Norm EN 166:1995 (einer umfassenderen Norm für den persönlichen Augenschutz) und entweder der Norm EN 169:1992 oder der Norm EN 379:1994 (Normen für Schweißerschutzfilter bzw. Automatikschweißhelme) entsprechen.
3. Anwendungsbereich und Ausschlüsse
DE 175 definiert den Anwendungsbereich der Norm und legt fest, welche Arten von PSA sie abdeckt. Sie schließt Augen- und Gesichtsschutzgeräte ein, die speziell für das Schweißen, Schneiden und verwandte Verfahren entwickelt wurden. Es wird jedoch ausdrücklich darauf hingewiesen, dass Hauben, Gesichtsschutz für Inspektoren, Laserschutzausrüstung und Schweißerschutz für spezielle Anwendungen nicht in den Anwendungsbereich dieser Norm fallen.
4. Terminologie und Produktanforderungen
Die Norm enthält eine Reihe gemeinsamer Begriffe und Definitionen, die im Zusammenhang mit dem Schweißen und verwandten Verfahren verwendet werden, um Klarheit und Konsistenz in der Kommunikation zu gewährleisten. Außerdem werden Anforderungen an Produktdesigns, Werkstoffe und Herstellungsverfahren festgelegt. Diese Anforderungen tragen dazu bei, dass die PSA die erforderlichen Sicherheitsstandards erfüllt und die Arbeitnehmer wirksam schützen kann.
5. Einhaltung und Prüfung
Die Hersteller von PSA für das Schweißen und verwandte Verfahren müssen sich an Folgendes halten DE 175 Normen und unterziehen sich strengen Tests, um zu überprüfen, ob ihre Produkte die festgelegten Sicherheitsanforderungen erfüllen. Durch die Einhaltung dieser Normen wird sichergestellt, dass die PSA den Anwendern einen angemessenen Schutz vor den verschiedenen Gefahren bietet.
Zusammengefasst, DE 175 ist eine wichtige europäische Norm, die Sicherheitsanforderungen und Prüfverfahren für persönliche Schutzausrüstungen zum Schutz der Augen und des Gesichts von Arbeitnehmern festlegt, die mit Schweißen, Schneiden und ähnlichen industriellen Verfahren arbeiten. Durch die Einhaltung der DE 175können die Hersteller sicherstellen, dass ihre Produkte einen zuverlässigen Schutz bieten und die Sicherheit und das Wohlbefinden von Personen fördern, die in diesen risikoreichen Umgebungen arbeiten.
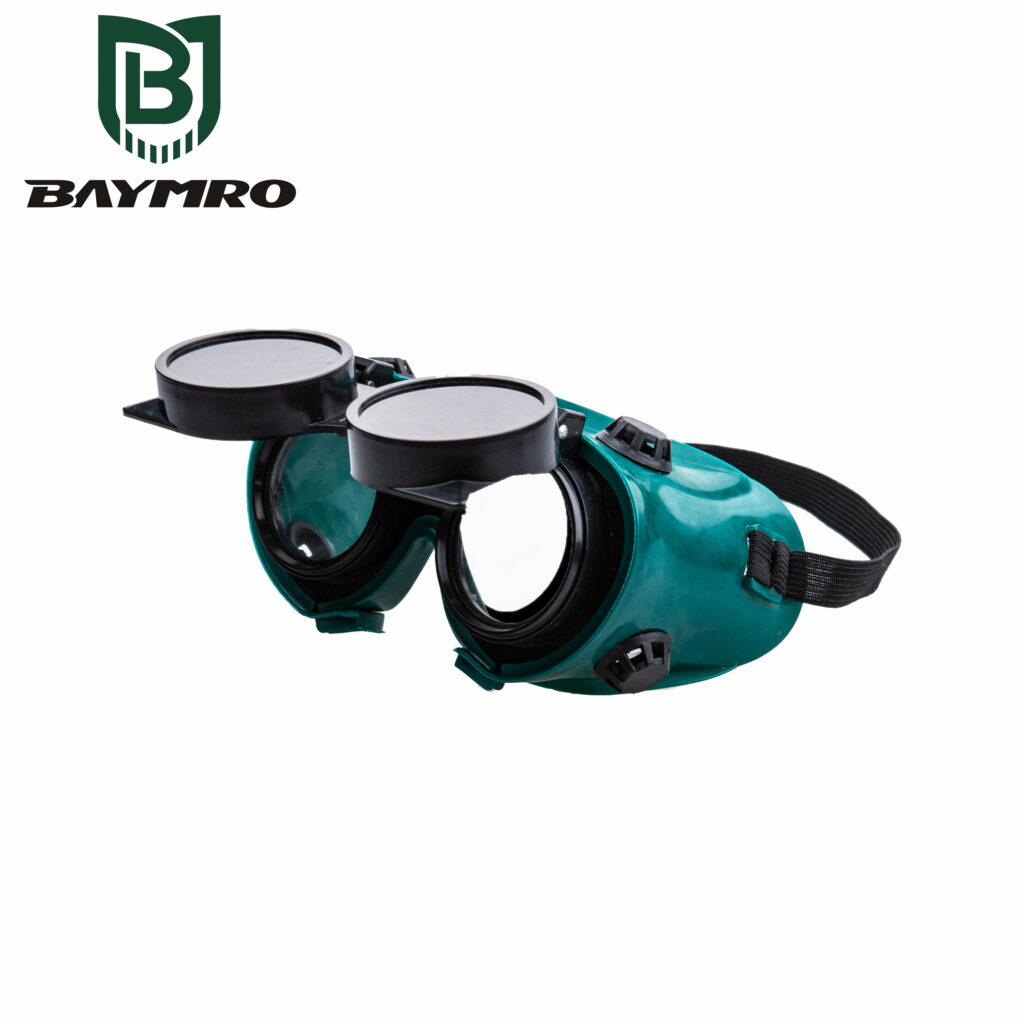

EN 169 ist in der Tat eine wichtige europäische Norm für den persönlichen Augenschutz, die sich speziell auf Filter für das Schweißen und verwandte Techniken bezieht. Diese Norm stellt sicher, dass Augenschutzgeräte, die in Schweißumgebungen verwendet werden, strenge Anforderungen erfüllen, um die Augen des Trägers vor den verschiedenen Gefahren zu schützen, die mit Schweißprozessen verbunden sind.
Hier ein genauerer Blick auf die wichtigsten Aspekte von DE 169 und warum sie für die Sicherheit beim Schweißen und in ähnlichen risikoreichen Umgebungen unerlässlich ist:
1. Schweißen und verwandte Techniken
EN 169 befasst sich in erster Linie mit dem Augenschutz beim Schweißen und verwandten Techniken. Beim Schweißen entstehen intensives Licht, Hitze und Funken, was diese Tätigkeit zu einer Gefahr für die Augen macht. Daher ist ein spezieller Augenschutz unerlässlich, um Verletzungen zu vermeiden, die durch diese schweißbedingten Gefahren verursacht werden.
2. Widerstand gegen Flammen und heiße Partikel
Eines der wichtigsten Merkmale der DE 169 konformen Augenschutzes ist seine Beständigkeit gegen Flammen und heiße Partikel. In Schweißumgebungen können geschmolzenes Metall und Funken eine ernste Gefahr für die Augen darstellen. DE 169 Konforme Schutzausrüstung ist so konzipiert, dass sie diesen Bedingungen standhält und die Wahrscheinlichkeit von Verbrennungen und Verletzungen verringert.
3. Eignung für gefährliche Umgebungen
DE 169 Der konforme Augenschutz eignet sich gut für die gefährlichsten Schweißumgebungen, einschließlich industrieller Umgebungen, in denen Lichtbogenschweißen, Gasschweißen und andere Schweißtechniken üblicherweise eingesetzt werden. In diesen Umgebungen herrschen oft hohe Temperaturen, Funkenflug und die Möglichkeit, schädlicher UV- und Infrarotstrahlung ausgesetzt zu sein, was alles einen speziellen Schutz erfordert.
4. Objektivfilter und Shade-Nummern
Die Norm legt die Leistungsanforderungen für Linsenfilter fest, die für Schweißerschutzbrillen verwendet werden. Sie definiert auch Tönungszahlen, die den Grad des Schutzes gegen das beim Schweißen erzeugte intensive Licht angeben. Die Wahl der Tönungszahl hängt von dem jeweiligen Schweißverfahren und der Intensität des erzeugten Lichts ab.
5. Benutzerkomfort und Sichtbarkeit
Sicherheit ist zwar oberstes Gebot, DE 169 Der konforme Augenschutz wurde auch im Hinblick auf Benutzerkomfort und Sichtbarkeit entwickelt. Eine klare Sicht ist für Schweißer entscheidend, damit sie ihre Aufgaben präzise ausführen können. Daher sind diese Schutzgläser so konstruiert, dass sie den notwendigen Schutz bieten und gleichzeitig sicherstellen, dass Schweißer ihre Arbeit deutlich sehen können.
6. Sicherstellung der Einhaltung
Hersteller von Augenschutzgeräten, die sich an die DE 169 müssen sich strengen Prüfungen unterziehen, um sicherzustellen, dass ihre Produkte die festgelegten Anforderungen erfüllen. Die Einhaltung der Norm bietet den Benutzern Vertrauen in die Qualität und Wirksamkeit der Schutzausrüstung.
Zusammengefasst, DE 169 ist eine wichtige europäische Norm, die den Maßstab für den persönlichen Augenschutz beim Schweißen und verwandten Techniken setzt. Sie stellt sicher, dass die Augenschutzausrüstung gegen Flammen und heiße Partikel resistent ist und somit auch in den gefährlichsten Schweißumgebungen eingesetzt werden kann. Übereinstimmung mit DE 169 ist für die Sicherheit und das Wohlergehen von Schweißern und Arbeitnehmern, die ähnlichen Risikobedingungen ausgesetzt sind, unerlässlich.
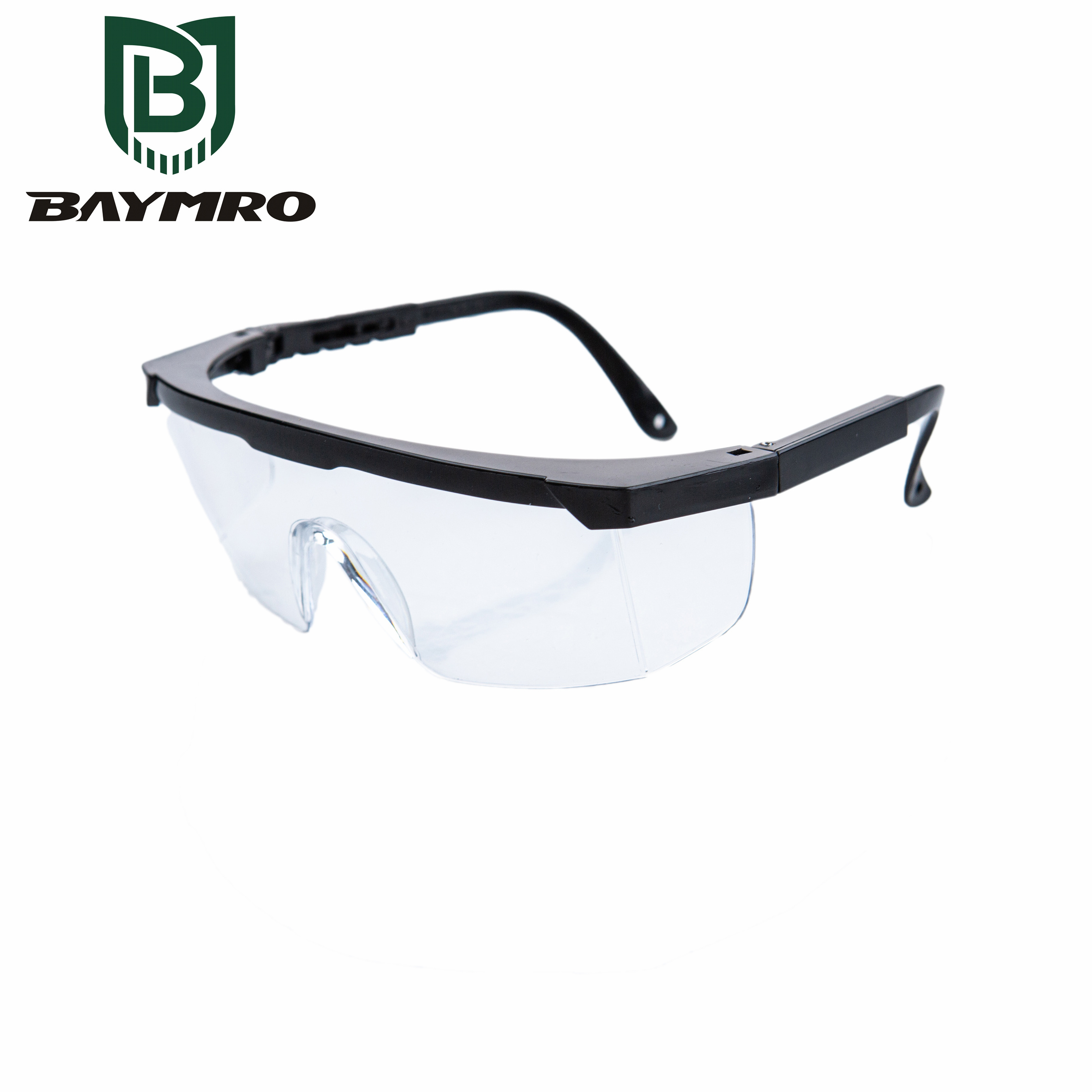

Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is a potent threat to our eyes, and prolonged exposure can lead to various eye conditions and even blindness. To safeguard against such risks, European Standard EN 170:2002 was developed. This standard sets forth the requirements and guidelines for ultraviolet filters used in personal eye protection. In this article, we’ll delve into the key aspects of EN 170:2002.

1. Purpose of EN 170:2002
EN 170:2002 primarily focuses on ultraviolet filters and their transmittance requirements. These filters are designed to protect the eyes from harmful UV radiation, which can originate from various sources, including the sun and certain industrial processes. The standard establishes standards for the performance of these filters and provides guidance on their use.
2. Transmittance Requirements
The standard specifies both scale numbers and transmittance requirements for ultraviolet filters. Transmittance refers to the amount of UV radiation that can pass through the filter. By setting clear requirements, EN 170 ensures that these filters provide effective protection against harmful UV rays.
3. Compatibility with EN 166
EN 166 is another European standard that addresses personal eye protection, covering a wide range of eye protection equipment. EN 170 complements EN 166 by focusing specifically on the requirements for ultraviolet filters. The frames and mountings to which these filters are affixed must comply with the applicable requirements in EN 166. This ensures that the complete eye protection apparatus is safe and reliable.
4. Selection and Use Guidance
Annex B of EN 170:2002 provides valuable guidance on the selection and use of ultraviolet filters. It assists users in choosing the right filter for their specific applications and highlights best practices for their proper utilization. This guidance enhances user safety and the effectiveness of the protective filters.
5. Limitations
It’s important to note that the protective filters discussed in EN 170 are not suitable for direct viewing of intense sources of bright light, such as Xenon high-pressure arc lamps. Additionally, they are not intended for direct or indirect observation of an electric welding arc. These situations require specialized eye protection equipment designed to handle extremely high-intensity light sources.
6. Marking and Numbering
EN 170 references the numbering table for filters and provides guidelines for marking oculars (lenses) and frames of eye protection equipment. Proper marking helps users identify the level of protection and ensures compliance with the standard.
Zusammengefasst, EN 170:2002 is a vital European standard that addresses the protection of the eyes from harmful ultraviolet radiation. It sets out clear requirements for ultraviolet filters and offers guidance on their selection and use. By adhering to EN 170, individuals and employers can ensure that their eye protection equipment provides adequate defense against UV radiation, helping to safeguard eye health in various settings.
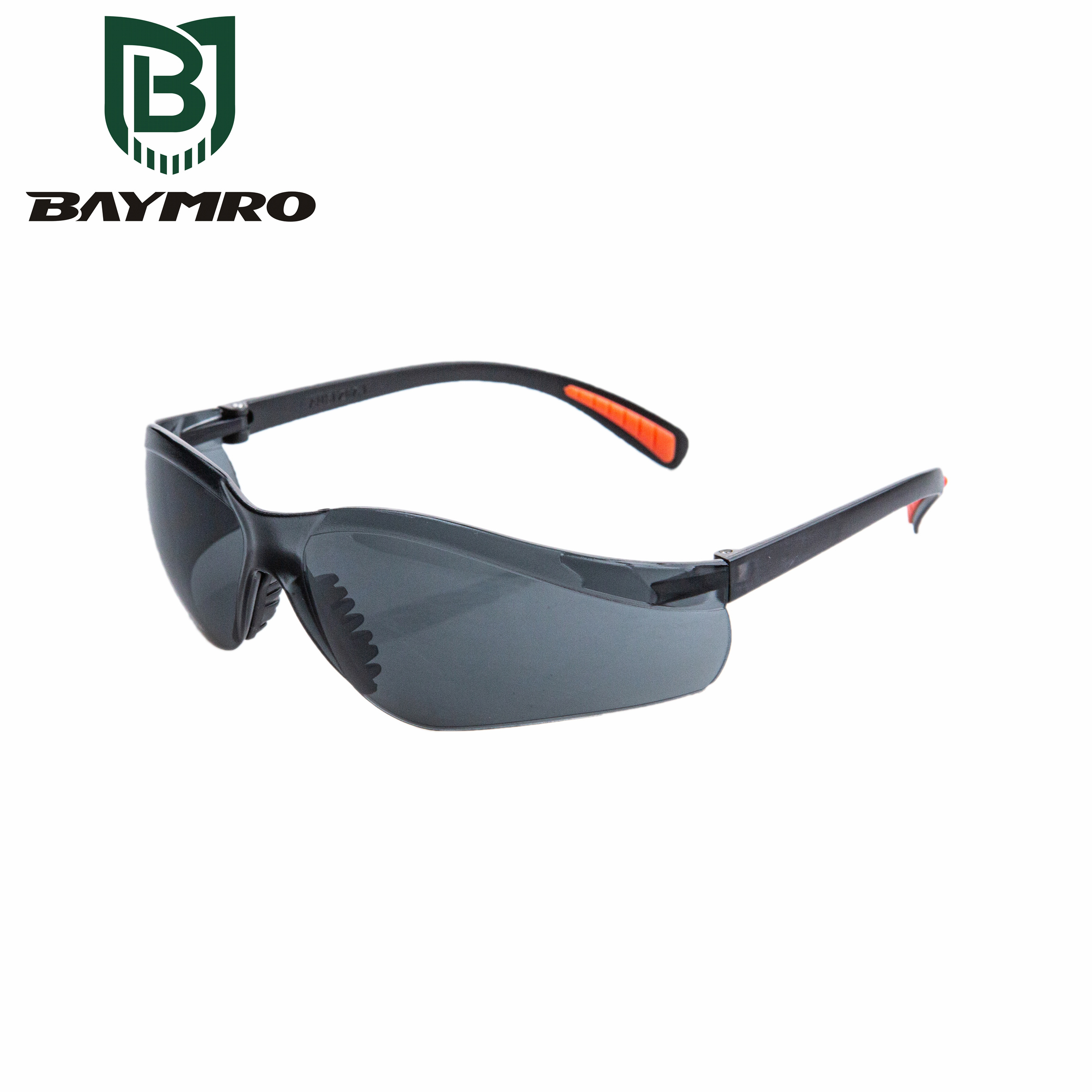

EN 166 is a European standard that pertains to personal eye protection. It specifies the requirements and testing methods for various types of eye protection equipment to ensure their safety and effectiveness. EN 166 is important for ensuring that eye protection devices are suitable for their intended purposes and provide adequate protection against various hazards, including mechanical, chemical, optical, and thermal risks. Let’s break down the key components and aspects of EN 166:
Scope: EN 166 covers a wide range of personal eye protection equipment, including safety glasses, goggles, face shields, welding helmets, and more. It applies to both prescription and non-prescription eyewear.
Classification of Eye Protection: EN 166 classifies eye protection equipment into different categories based on their intended use and the level of protection they provide. The most common classifications include:
- EN 166 F: Basic impact protection for low-energy impacts, such as common industrial activities.
- EN 166 B: Higher impact protection for medium-energy impacts, often used in construction and similar applications.
- EN 166 A: Highest impact protection for high-energy impacts, suitable for more extreme industrial environments.
- EN 166 3: Protection against liquid droplets and splashes.
- EN 166 4: Protection against large dust particles.
- EN 166 5: Protection against gas and fine dust particles.
- EN 166 8: Protection against short circuit electric arcs.
- EN 166 9: Protection against molten metals and hot solids.
- EN 166 K: Resistance to surface damage by fine particles.
Optical Properties: EN 166 also specifies requirements for the optical properties of eye protection equipment, including clarity, distortion, and transmission of light. This ensures that the wearer can see clearly while using the protection.
Frame and Material Requirements: The standard includes guidelines for the materials used in the eyewear, such as frames and lenses, to ensure durability and safety.
Marking and Labeling: Eye protection devices compliant with EN 166 must be marked with relevant symbols and information. These markings indicate the type of protection offered and other essential details, such as the manufacturer’s information.
Testing: EN 166 outlines rigorous testing procedures that eye protection equipment must undergo to ensure their compliance with safety standards. These tests evaluate resistance to impact, penetration, optical quality, and more.
User Instructions: Manufacturers are required to provide clear and comprehensive user instructions to ensure that wearers understand how to properly use and maintain the eye protection equipment.
Compatibility: When applicable, the standard may also specify compatibility requirements with other personal protective equipment (PPE) items, such as respiratory protection.
It’s crucial for employers and individuals to choose eye protection equipment that complies with EN 166 standards to ensure the safety of workers and users in various industrial and hazardous environments. Compliance with these standards helps reduce the risk of eye injuries and ensures that eye protection equipment performs as intended. Keep in mind that while EN 166 is specific to the European Union, similar standards exist in other regions, such as ANSI Z87.1 in the United States.
Titel: Gewährleistung der Sicherheit bei der Arbeit mit Kettensägen: Ein Leitfaden zu EN ISO 11393-4:2019
2023

Einführung
Working with hand-held chainsaws is a task that requires precision, skill, and, most importantly, safety precautions. Chainsaw operators face inherent dangers, and protecting oneself from the risks associated with this equipment is paramount. That’s where standards like EN ISO 11393-4:2019 come into play. This standard, titled “Protective clothing for users of hand-held chainsaws – Part 4: Performance requirements and test methods for protective gloves,” serves as a crucial resource for ensuring the safety of individuals operating chainsaws.
Understanding EN ISO 11393-4:2019
EN ISO 11393-4:2019 is a part of the broader ISO 11393 series, which focuses on protective clothing for users of hand-held chainsaws. Specifically, this standard centers on protective gloves, a vital component of chainsaw operator safety. Chainsaw users face potential hazards, including cuts from the chainsaw chain, making protective gloves an indispensable element of their safety gear.
Performance Requirements
One of the primary functions of EN ISO 11393-4:2019 is to outline performance requirements for protective gloves. These requirements are designed to ensure that gloves effectively shield users from chainsaw-related dangers. The standard specifies the materials, construction, and performance criteria that gloves must meet to provide reliable protection.
Test Methods
To determine whether protective gloves meet the performance requirements, EN ISO 11393-4:2019 provides comprehensive test methods. These tests assess the gloves’ resistance to cutting by chainsaw chains and other relevant performance factors. Rigorous testing ensures that the gloves meet specific safety and protection standards.
Design Specifications
The standard also lays out design specifications for protective gloves. This includes factors such as glove construction, sizing, and ergonomic considerations. Proper design ensures that the gloves are not only protective but also comfortable and functional for the wearer.
Identification and Marking
EN ISO 11393-4:2019 includes guidelines for labeling and marking protective gloves. This is crucial for users to identify gloves that meet the standard’s safety requirements. The markings provide information about the gloves’ protective capabilities and their compliance with the standard.
Annex A: Guidance on Chainsaw Use
Annex A of the standard offers additional guidance on chainsaw use and the selection of gloves. It serves as a valuable resource for chainsaw operators, helping them understand the safe operation of chainsaws while emphasizing the importance of selecting appropriate protective gloves.
Schlussfolgerung
Operating hand-held chainsaws is a task that demands precision and safety. EN ISO 11393-4:2019 plays a pivotal role in ensuring the well-being of chainsaw operators. By setting performance requirements, test methods, design specifications, and providing guidance on chainsaw use and glove selection, this standard promotes a safer working environment. Chainsaw operators and stakeholders can rely on EN ISO 11393-4:2019 to make informed choices when it comes to protective gloves, ultimately reducing the risks associated with chainsaw operations and enhancing workplace safety.
 3M
3M Ansell
Ansell Dellta Plus
Dellta Plus Drager
Drager edelrid
edelrid Honeywell
Honeywell JUTEC
JUTEC Seeland
Seeland MSA
MSA Neues Schwein
Neues Schwein Weldas
Weldas