Archive for the ‘Blog’ Category
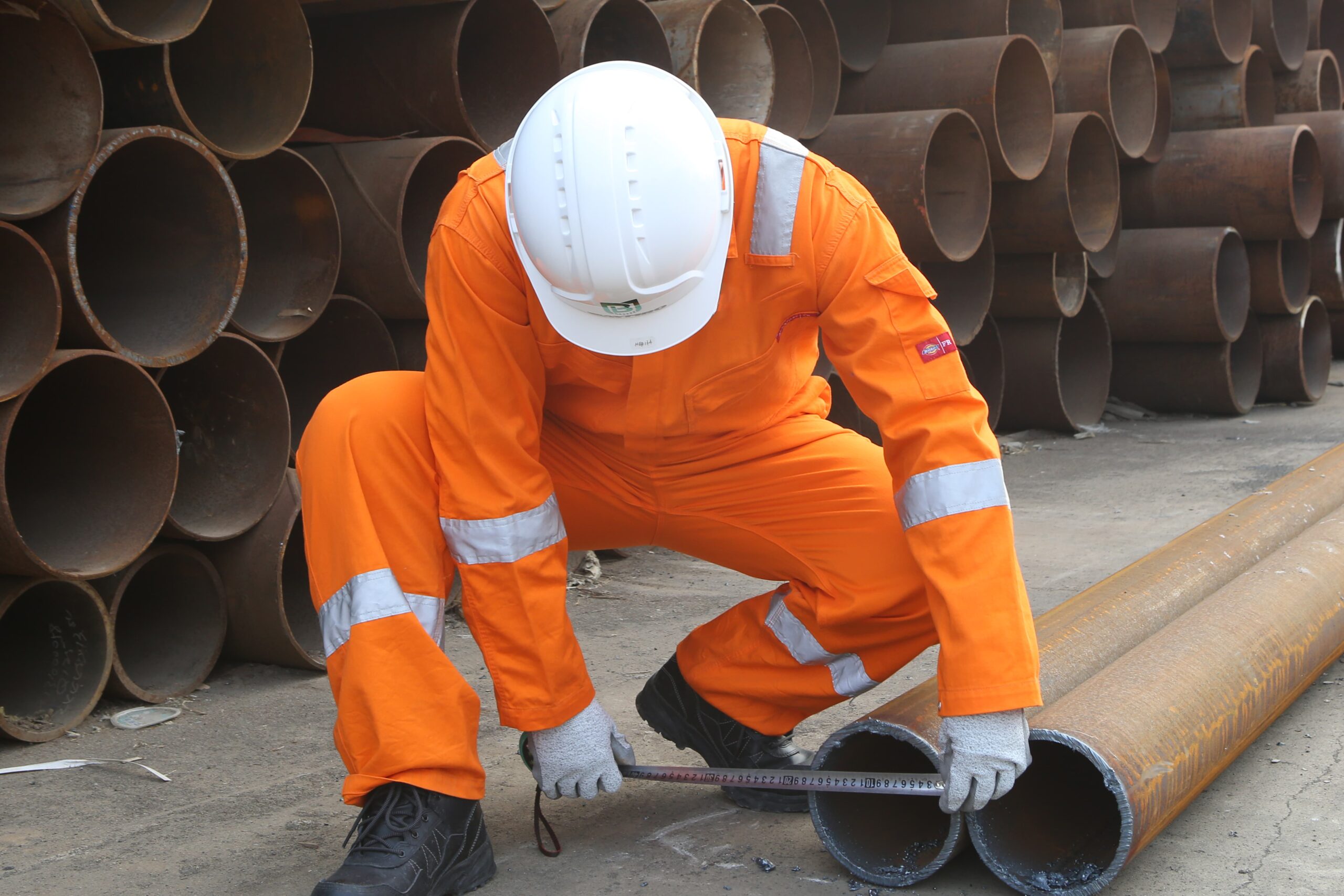


Introduction
Personal Protective Equipment, commonly known as PPE, is a vital component of workplace safety across various industries and has taken on newfound importance in our daily lives during the COVID-19 pandemic. PPE serves as a shield, safeguarding individuals from a range of potential hazards, ensuring their well-being, and enabling them to perform their tasks effectively. In this article, we will delve into the world of PPE, discussing what it is, its classifications, common usage scenarios, and how to choose the right PPE for specific situations.
What is PPE?
Personal Protective Equipment, or PPE, refers to specialized gear, equipment, or clothing designed to protect individuals from workplace or environmental hazards that could cause injury, illness, or even death. PPE acts as a barrier between the wearer and various risks, including physical, chemical, biological, radiological, and electrical dangers.
Classifications of PPE
PPE can be classified into several categories, each tailored to address specific types of hazards. The primary classifications include:
Head Protection: This category includes safety helmets or hard hats, which shield the head from falling objects, electrical shocks, and impacts. They are commonly used in construction and industrial settings.
Eye and Face Protection: Safety glasses, goggles, and face shields protect the eyes and face from flying debris, chemicals, intense light, and splashes. These are essential in industries like welding, woodworking, and laboratories.
Hearing Protection: Earplugs and earmuffs are used to reduce exposure to high noise levels, preventing hearing loss in noisy work environments, such as manufacturing plants or construction sites.
Respiratory Protection: Respirators, including N95 masks and full-face respirators, filter out harmful particles and contaminants from the air. They are critical in healthcare, construction, and industries dealing with airborne hazards.
Hand and Arm Protection: Gloves, sleeves, and gauntlets are used to protect hands and arms from cuts, chemical exposure, burns, and abrasions. Workers in healthcare, manufacturing, and laboratories frequently use these.
Body Protection: This category includes coveralls, aprons, and vests, designed to safeguard the torso and limbs from chemical, biological, radiological, or physical hazards. Industries such as healthcare, hazardous material handling, and agriculture employ body protection.
Foot and Leg Protection: Safety boots or shoes with reinforced toes and slip-resistant soles protect the feet from falling objects, punctures, electrical hazards, and slips. They are indispensable in construction, manufacturing, and mining.
Fall Protection: Harnesses, lanyards, and lifelines are essential for preventing falls from heights and are commonly used in construction, maintenance, and roofing.
Scenarios of PPE Usage
PPE finds application in a wide range of scenarios:
Healthcare: Healthcare workers use PPE such as masks, gloves, gowns, and face shields to protect themselves and patients from infections and other hazards.
Construction: Construction workers rely on PPE like hard hats, safety vests, gloves, and fall protection equipment to mitigate the risks of falling objects, slips, trips, and falls.
Chemical Handling: Workers handling chemicals use PPE like chemical-resistant suits, gloves, and goggles to prevent exposure to corrosive or toxic substances.
Welding: Welders wear helmets with face shields, welding gloves, and flame-resistant clothing to shield themselves from intense heat and UV radiation.
Manufacturing: Employees in manufacturing industries use PPE like safety glasses, hearing protection, and protective clothing to stay safe from various workplace hazards.
How to Choose PPE
Selecting the right PPE is crucial for safety. Here are some steps to guide you in making the correct choices:
Identify Hazards: Conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify potential hazards in your work environment.
Understand Regulations: Familiarize yourself with local and national regulations and standards governing PPE use in your industry.
Select Appropriate PPE: Choose PPE that is specifically designed to protect against the identified hazards. Ensure it fits properly and is comfortable to wear for extended periods.
Training and Education: Train employees on the proper use, maintenance, and limitations of PPE. Make sure they understand when and how to use it.
Regular Maintenance: Inspect and maintain PPE regularly to ensure it remains effective. Replace damaged or worn-out equipment promptly.
Evaluate and Adjust: Continuously evaluate your PPE program and make necessary adjustments based on feedback and changing workplace conditions.
Conclusion
Remember that your safety should always be a top priority. Properly selected and maintained PPE plays a crucial role in reducing the risks associated with various workplace hazards.
GB 14866-2006 is a Chinese national standard that sets forth the specifications and requirements for safety glasses. Developed by the Standardization Administration of China (SAC), this standard is crucial for ensuring the safety of individuals who use protective eyewear in various industrial and occupational settings within China. Here’s an overview of GB 14866-2006:

1. Purpose and Scope
GB 14866-2006 primarily focuses on safety glasses used to protect the eyes from various hazards, including mechanical impacts, chemical splashes, dust, and optical radiation. The standard aims to establish a consistent framework for the design, testing, and performance of these protective glasses.
2. Types of Protection
This standard covers a range of protective eyewear, including safety glasses, goggles, and face shields. These devices are designed to safeguard the eyes against different risks commonly encountered in industrial, construction, laboratory, and other work environments.
3. Design Requirements
GB 14866-2006 outlines design requirements for safety glasses, ensuring they provide comprehensive protection without compromising comfort and usability. These requirements encompass factors such as impact resistance, optical clarity, and frame construction.
4. Testing Procedures
Safety glasses that comply with GB 14866-2006 must undergo rigorous testing procedures to verify their compliance with the standard. These tests evaluate various aspects of performance, including impact resistance, optical quality, and resistance to environmental factors.
5. Marking and Labeling
Products that meet the GB 14866-2006 standard must be marked and labeled accordingly. These markings typically include information about the manufacturer, product model, and compliance with the standard. Such markings help users identify suitable eyewear for their specific needs.
6. Workplace Safety
Compliance with GB 14866-2006 is essential for maintaining workplace safety in China. Employers are often required to provide and enforce the use of GB-compliant protective eyewear to reduce the risk of eye injuries in hazardous work environments.
7. Compatibility
GB 14866-2006 is often compatible with other Chinese workplace safety standards, allowing for a comprehensive approach to employee protection. This compatibility ensures that various aspects of safety gear, such as head protection or respiratory protection, can work together effectively.
In summary, GB 14866-2006 is a crucial Chinese national standard that sets the requirements for safety glasses and protective eyewear used in a variety of work environments. Compliance with this standard helps mitigate the risk of eye injuries and promotes a safer and healthier workplace in China. Users and employers should ensure that the eyewear they use meets GB 14866-2006 standards to enhance safety and reduce the risk of accidents and injuries in the workplace.
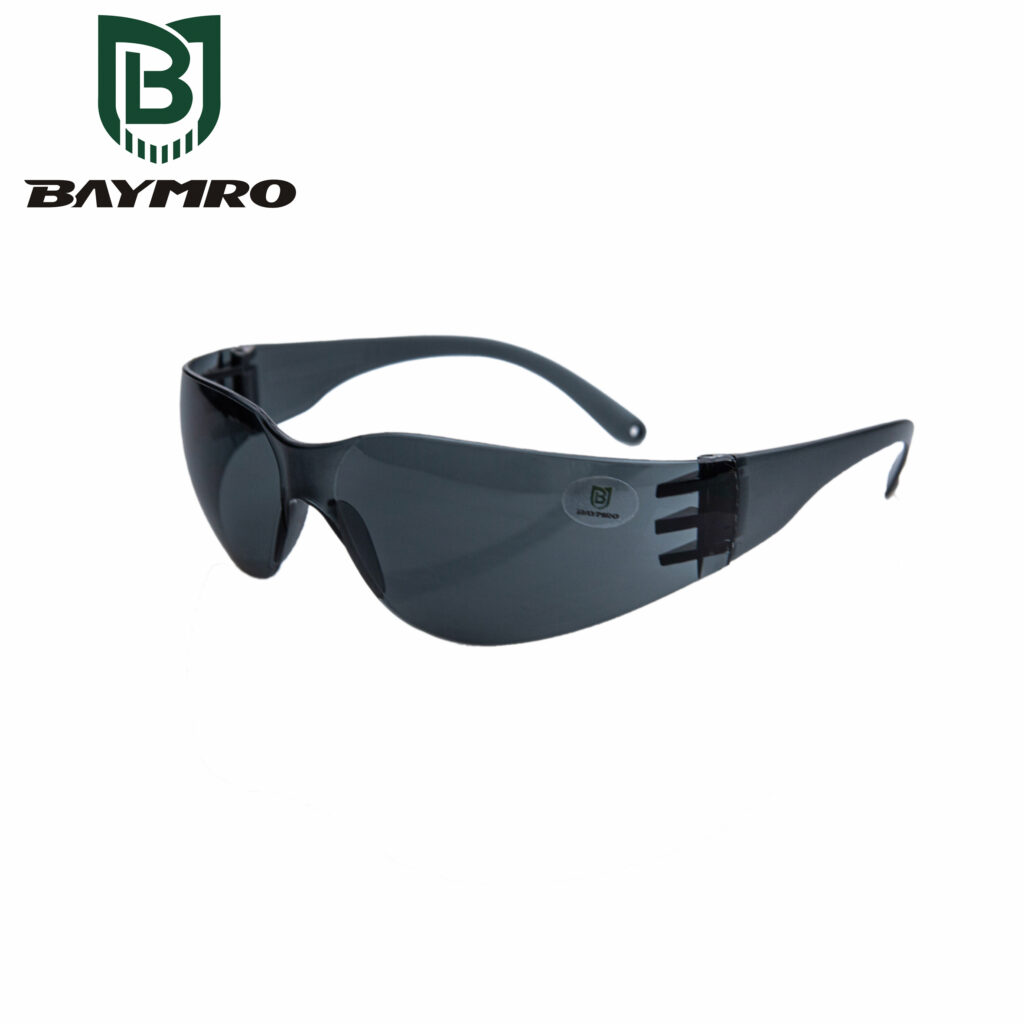


ANSI Z87.1 is an important standard developed by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) for the purpose of ensuring the safety and protection of industrial workers from various hazards that may affect the eyes and face. This standard specifically addresses eye and face protection products, such as safety glasses, goggles, face shields, welding helmets, and more. Let’s break down what ANSI Z87.1 signifies and its significance:
1. Purpose of ANSI Z87.1
ANSI Z87.1 serves as a comprehensive set of guidelines and requirements aimed at safeguarding the eyes and face of workers in industrial and occupational settings. The standard is designed to enhance workplace safety by establishing stringent criteria for the design, testing, and performance of protective eyewear and face shields.
2. Types of Protection Covered
ANSI Z87.1 covers a wide range of eye and face protection products, including:
Safety Glasses: Protective eyewear designed to shield the eyes from various hazards, including impact, chemicals, and UV radiation.
Goggles: Goggles provide a more comprehensive seal around the eyes, offering protection against splashes, dust, and chemical hazards.
Face Shields: These protective devices cover the entire face and offer additional protection against impact, chemical splashes, and other hazards. They are often used in conjunction with other eyewear.
Welding Helmets: Helmets designed for welding applications that provide protection against intense light, heat, and flying debris.
3. Design Requirements
The standard outlines design requirements for eye and face protection products. These requirements include specifications for impact resistance, optical clarity, and frame construction. Impact resistance ensures that the protective equipment can withstand a certain level of force without breaking or shattering, providing effective protection in the event of an impact.
4. Testing Requirements
ANSI Z87.1 includes rigorous testing requirements that products must undergo to demonstrate their compliance with the standard. These tests evaluate various aspects of performance, such as impact resistance, optical quality, and resistance to environmental factors.
5. Marking and Labeling
Products that meet the ANSI Z87.1 standard are required to be marked and labeled accordingly. These markings indicate the level of protection offered and provide essential information about the manufacturer and product compliance.
6. Workplace Safety
The adoption of ANSI Z87.1 compliant eye and face protection products in the workplace helps ensure the safety and well-being of industrial workers. It reduces the risk of eye injuries from mechanical, chemical, and other hazards, making it an essential component of workplace safety programs.
In summary, ANSI Z87.1 is a crucial American standard that sets the bar for the design, testing, and performance of eye and face protection equipment used in industrial and occupational settings. Compliance with this standard is essential for employers and individuals to ensure that protective eyewear and face shields effectively mitigate the risks associated with various workplace hazards, promoting a safer work environment.
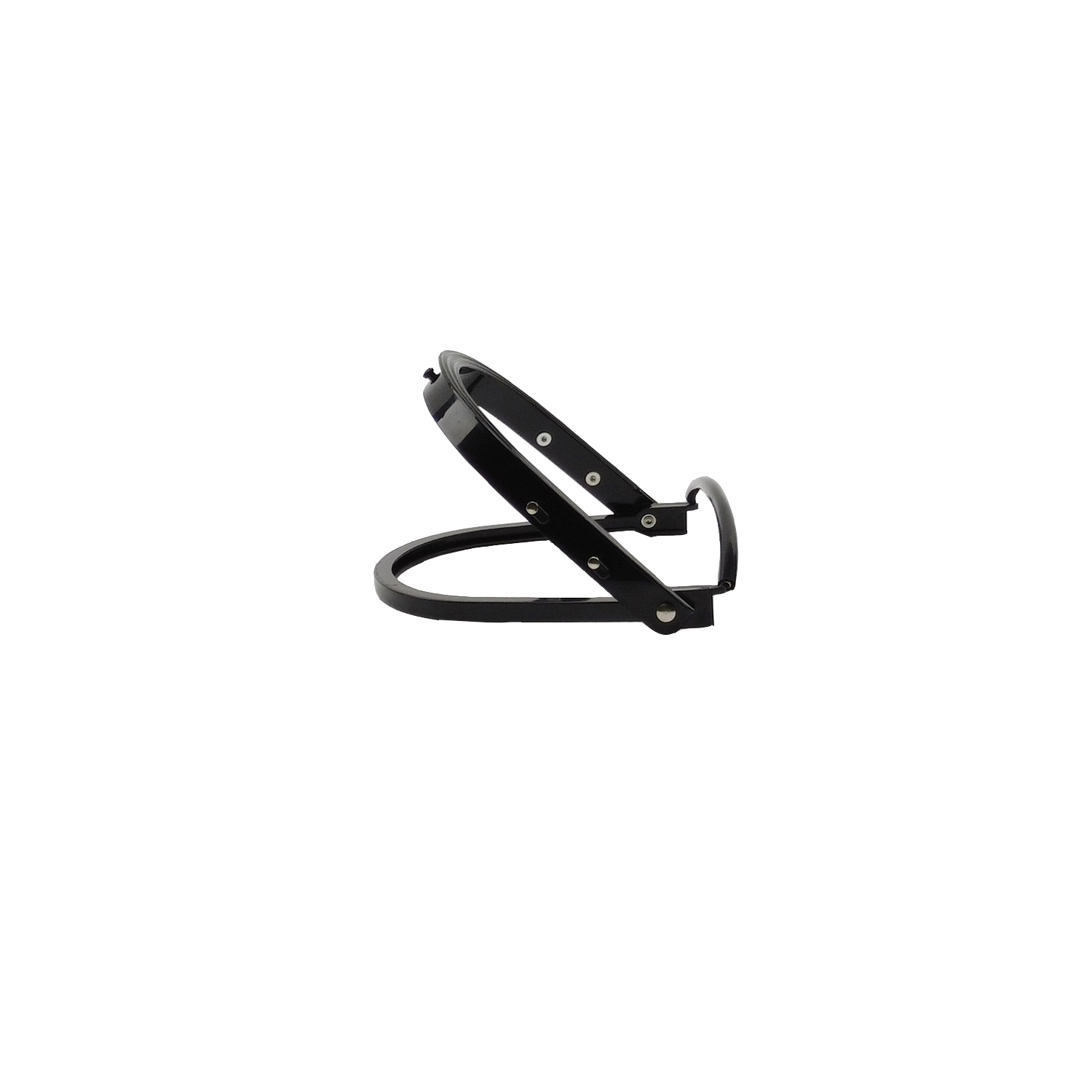

EN 1731 is a European standard that specifies the requirements for face shields designed to protect against various hazards, particularly mechanical ones. These face shields are essential safety equipment, providing reliable protection for the eyes and face. In this article, we’ll explore the key aspects of EN 1731 and understand its significance in ensuring safety in professional and industrial settings.
1. Material Specifications
EN 1731 outlines material specifications, ensuring that face mesh protectors are constructed from materials that can withstand mechanical hazards. These materials are chosen for their durability and ability to provide effective protection against impacts, flying debris, and other potential dangers.
2. Design Requirements
The standard also defines design requirements for face shields, ensuring that they provide adequate coverage for the eyes and face. Proper design is crucial to ensure that the protector offers comprehensive protection without hindering the wearer’s vision or comfort.
3. Performance Standards
EN 1731 sets performance standards for face mesh protectors, specifying the level of protection they should provide. This includes protection against impacts, such as those caused by flying objects, projectiles, or other mechanical hazards. Meeting these performance standards is essential to ensure that the protector effectively safeguards the wearer.
4. Test Methods
The standard includes detailed test methods that manufacturers must follow to assess the performance of their face mesh protectors. These tests help ensure that the protectors meet the required safety standards. Common tests may include impact resistance tests and tests for the integrity of the mesh material.
5. Reliable Protection
Face mesh protectors that conform to EN 1731 are known for their reliability in protecting against mechanical hazards. They are particularly suitable for professional use in industrial and work environments where the risk of flying debris or other mechanical dangers is high.
6. Industrial Applications
EN 1731 compliant face shields are commonly used in various professional and industrial applications, including construction, manufacturing, forestry, and agriculture. They provide essential protection for workers exposed to potential hazards, reducing the risk of eye and face injuries.
7. User Comfort
While safety is paramount, EN 1731 also considers user comfort. Properly designed face shields are comfortable to wear for extended periods, ensuring that workers can perform their tasks effectively without discomfort.
In summary, EN 1731 is a crucial European standard that sets the requirements for face mesh protectors used in professional and industrial settings. These protectors are essential for safeguarding the eyes and face against mechanical hazards, making them a vital part of personal protective equipment. Choosing EN 1731 compliant face shields ensures that workers are adequately protected in environments where mechanical dangers are prevalent, promoting safety and reducing the risk of injuries.
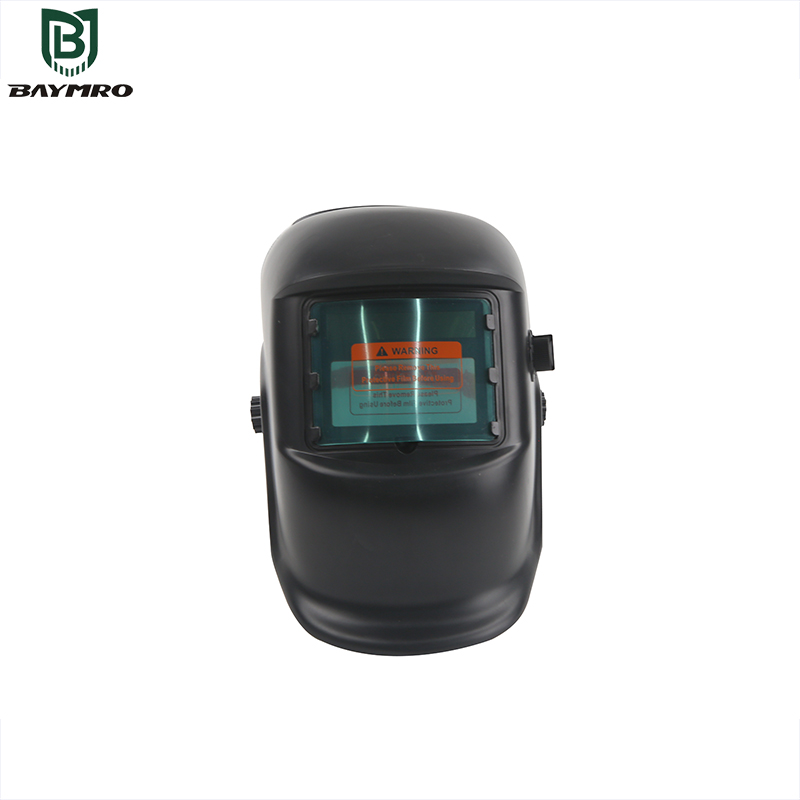


EN 379 is a European standard that lays down the specifications and testing procedures for automatic welding filters used in personal eye protection. These specialized filters are designed to automatically adjust their light transmission to provide optimal protection when a welding arc is ignited. This standard is crucial for ensuring the safety and comfort of welders by regulating the performance of these dynamic filters. Let’s delve into the key features and importance of EN 379:
https://baymrosafety.com/product-category/face-protection/
1. Resource Filters with Changeable Scale Numbers
EN 379 encompasses two types of automatic welding filters. The first type, referred to as “resource filters with changeable scale numbers,” allows users to manually adjust the filter’s scale number to achieve the desired level of light transmission when welding. This flexibility is valuable, as different welding processes and conditions may require varying degrees of protection.
2. Source Filters with Automatic Scale Number Adjustment
The second type of automatic welding filter addressed by EN 379 is known as “source filters with automatic scale number adjustment.” These filters are particularly innovative as they automatically adapt their light transmittance based on the intensity of the welding arc. When the welding arc is ignited, the filter quickly darkens to protect the welder’s eyes from the intense light and radiation. When the arc is extinguished, the filter returns to a clearer state to provide better visibility. This dynamic adjustment ensures that welders have the necessary protection without compromising their ability to see their work.
3. Continuous Monitoring and Ignition Period
EN 379 is significant in cases where automatic welding filters are used for continuous monitoring of the welding process and only during the ignition period of the arc. In such scenarios, the standard’s requirements ensure that the filters meet the necessary safety and performance criteria, allowing welders to work effectively and safely.
4. Compliance and Testing
Manufacturers of automatic welding filters must adhere to EN 379 standards and subject their products to rigorous testing. This testing verifies that the filters meet the specified requirements for performance, durability, and safety. Compliance with EN 379 gives users confidence that their eye protection equipment will provide reliable and consistent protection.
5. Turkish Standards Institute (TSE)
The Turkish Standards Institute (TSE) has adopted and published EN 379 as a national standard in Turkey. This means that manufacturers and users of automatic welding filters in Turkey must follow the requirements outlined in EN 379 to ensure the safety and effectiveness of these filters.
In summary, EN 379 is a crucial European standard that governs the performance and safety of automatic welding filters used in personal eye protection. These filters, whether resource filters with changeable scale numbers or source filters with automatic scale number adjustment, are vital for safeguarding welders’ eyes from the intense light and radiation generated during welding processes. Compliance with EN 379 standards is essential to ensure that these filters deliver reliable and adaptable protection to workers in welding environments.
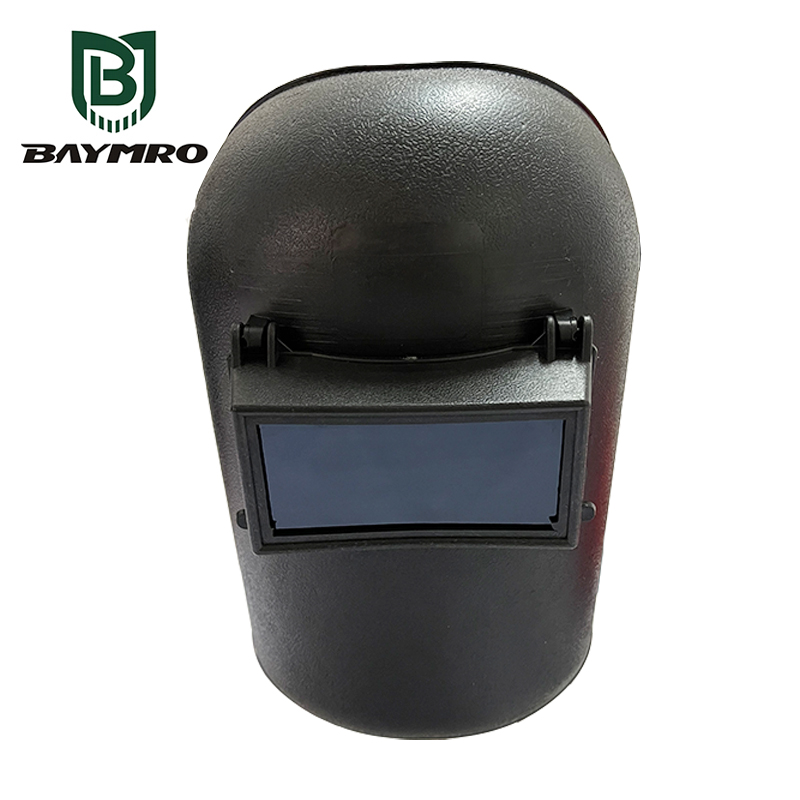

EN 175 is a European standard that outlines safety requirements and testing methods for personal protective equipment (PPE) designed to safeguard the eyes and face of workers engaged in welding, cutting, and similar operations. This standard is crucial for ensuring the safety of individuals exposed to the various hazards associated with these industrial processes. Let’s explore the key aspects of EN 175:
1. Protection Against Optical Radiation and Specific Hazards
EN 175 primarily focuses on PPE that protects against harmful optical radiation, such as the intense light and radiation generated during welding and cutting operations. It also addresses other specific risks and hazards associated with these processes, including ergonomic, fire, mechanical, and electrical risks.
2. Incorporation of Protective Filters
The standard mandates that the resulting PPE should incorporate protective filters, either with or without cover/backing oculars. These filters are crucial for shielding the eyes and face from the intense light and radiation produced during welding and similar tasks. The use of these filters is recommended by the welding protector manufacturer and must comply with EN 166:1995 (a broader standard for personal eye protection) and be in compliance with either EN 169:1992 or EN 379:1994 (standards related to welding filters and automatic welding helmets, respectively).
3. Scope and Exclusions
EN 175 defines the scope of the standard, specifying the types of PPE it covers. It includes eye and face protection equipment specifically designed for welding, cutting, and related processes. However, it explicitly states that hoods, inspector face screens, laser protective equipment, and welding protection for special applications fall outside the scope of this standard.
4. Terminology and Product Requirements
The standard provides a common set of terms and definitions used in the context of welding and related processes to ensure clarity and consistency in communication. It also specifies requirements for product designs, materials, and manufacturing processes. These requirements help ensure that the PPE meets the necessary safety standards and can effectively protect workers.
5. Compliance and Testing
Manufacturers of PPE designed for welding and related processes must adhere to EN 175 standards and undergo rigorous testing to verify that their products meet the specified safety requirements. Compliance with these standards ensures that the PPE offers adequate protection to users in the face of various hazards.
In summary, EN 175 is a critical European standard that sets forth safety requirements and testing methods for personal protective equipment designed to protect the eyes and face of workers engaged in welding, cutting, and similar industrial processes. By adhering to EN 175, manufacturers can ensure that their products provide reliable protection, promoting the safety and well-being of individuals working in these high-risk environments.
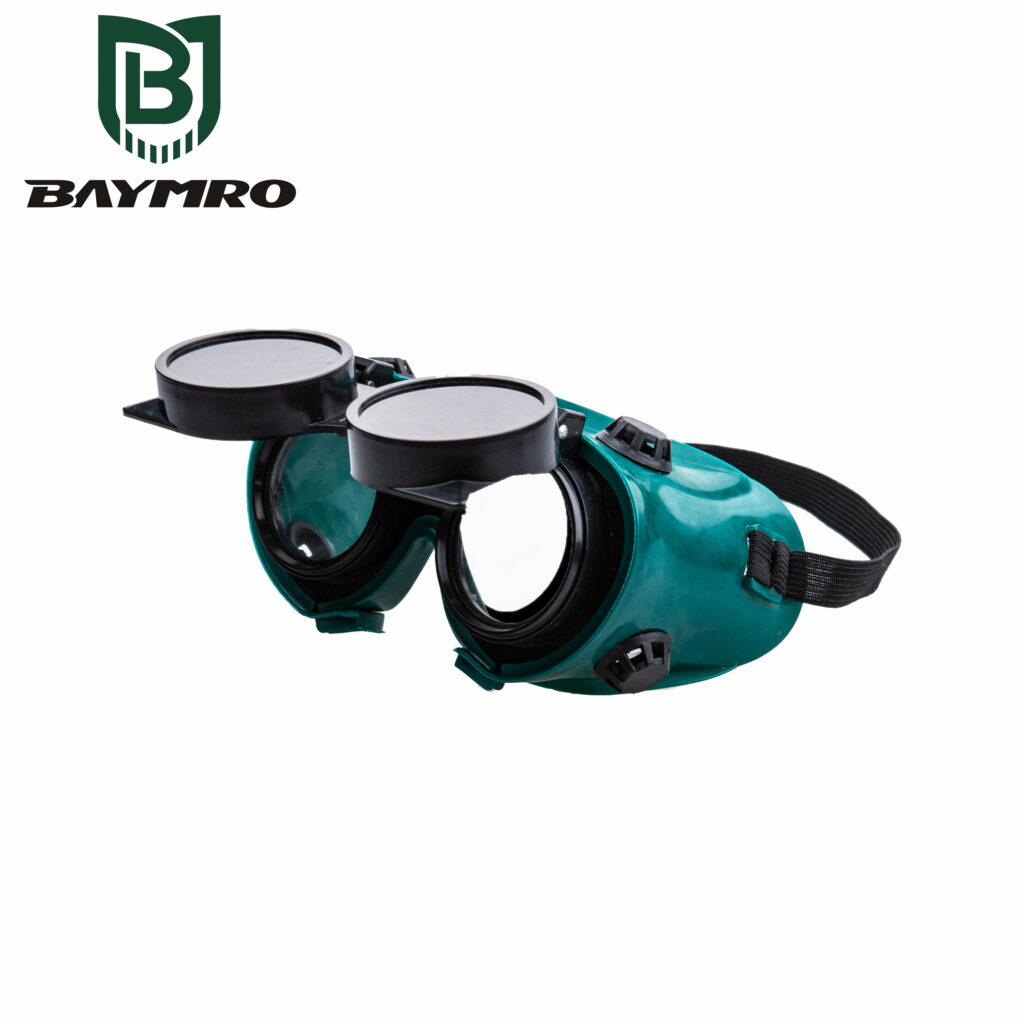

EN 169 is indeed an important European standard that pertains to personal eye protection, specifically focusing on filters designed for welding and related techniques. This standard ensures that eye protection equipment used in welding environments meets stringent requirements to safeguard the wearer’s eyes from the various hazards associated with welding processes.
Here’s a closer look at the key aspects of EN 169 and why it’s essential for ensuring safety in welding and similar high-risk environments:
1. Welding and Related Techniques
EN 169 primarily addresses eye protection for welding and related techniques. Welding generates intense light, heat, and sparks, making it a hazardous activity for the eyes. Therefore, specialized eye protection is crucial to prevent injuries caused by exposure to these welding-related hazards.
2. Flame and Hot Particle Resistance
One of the significant features of EN 169 compliant eye protection is its resistance to flames and hot particles. In welding environments, molten metal and sparks can pose a serious risk to the eyes. EN 169 compliant protective equipment is designed to withstand these conditions, reducing the likelihood of burns and injuries.
3. Hazardous Environment Suitability
EN 169 compliant eye protection is well-suited for the most hazardous welding environments, including industrial settings where arc welding, gas welding, and other welding techniques are commonly used. These environments often involve high temperatures, flying sparks, and the potential for exposure to harmful UV and infrared radiation, all of which require specialized protection.
4. Lens Filters and Shade Numbers
The standard specifies the performance requirements for lens filters used in welding eye protection. It also defines shade numbers that indicate the level of protection provided against the intense light generated during welding. The choice of shade number depends on the specific welding process and the intensity of the light produced.
5. User Comfort and Visibility
While safety is paramount, EN 169 compliant eye protection is also designed with user comfort and visibility in mind. Clear vision is crucial for welders to perform their tasks accurately. Therefore, these protective lenses are engineered to provide the necessary protection while ensuring that welders can see their work clearly.
6. Compliance Assurance
Manufacturers of eye protection equipment that adhere to EN 169 standards must undergo rigorous testing to ensure their products meet the specified requirements. Compliance with the standard offers users confidence in the quality and effectiveness of the protective equipment.
In conclusion, EN 169 is a critical European standard that sets the benchmark for personal eye protection in welding and related techniques. It ensures that eye protection equipment is resistant to flames and hot particles, making it ideal for use in the most hazardous welding environments. Compliance with EN 169 is essential for the safety and well-being of welders and workers exposed to similar high-risk conditions.
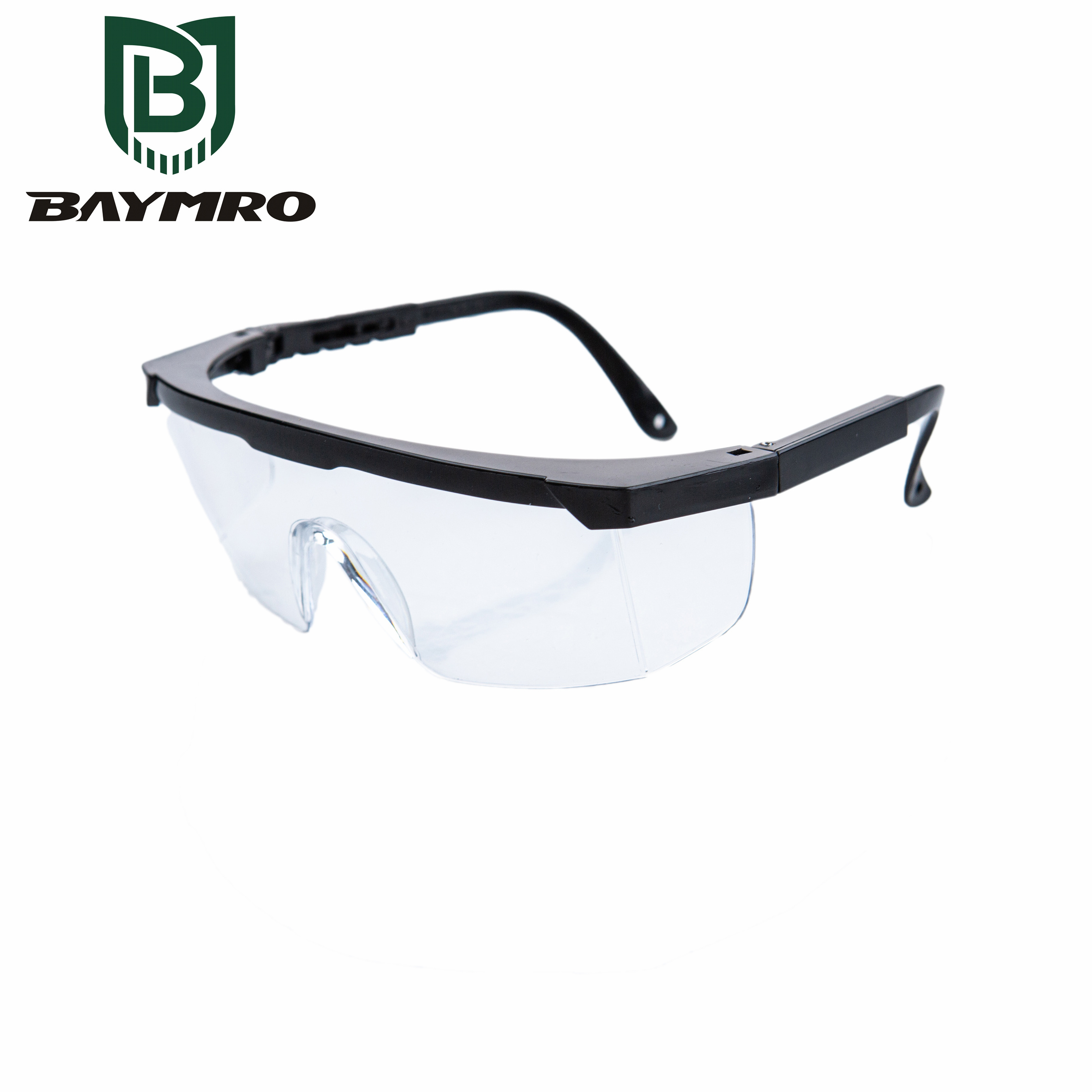

Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is a potent threat to our eyes, and prolonged exposure can lead to various eye conditions and even blindness. To safeguard against such risks, European Standard EN 170:2002 was developed. This standard sets forth the requirements and guidelines for ultraviolet filters used in personal eye protection. In this article, we’ll delve into the key aspects of EN 170:2002.

1. Purpose of EN 170:2002
EN 170:2002 primarily focuses on ultraviolet filters and their transmittance requirements. These filters are designed to protect the eyes from harmful UV radiation, which can originate from various sources, including the sun and certain industrial processes. The standard establishes standards for the performance of these filters and provides guidance on their use.
2. Transmittance Requirements
The standard specifies both scale numbers and transmittance requirements for ultraviolet filters. Transmittance refers to the amount of UV radiation that can pass through the filter. By setting clear requirements, EN 170 ensures that these filters provide effective protection against harmful UV rays.
3. Compatibility with EN 166
EN 166 is another European standard that addresses personal eye protection, covering a wide range of eye protection equipment. EN 170 complements EN 166 by focusing specifically on the requirements for ultraviolet filters. The frames and mountings to which these filters are affixed must comply with the applicable requirements in EN 166. This ensures that the complete eye protection apparatus is safe and reliable.
4. Selection and Use Guidance
Annex B of EN 170:2002 provides valuable guidance on the selection and use of ultraviolet filters. It assists users in choosing the right filter for their specific applications and highlights best practices for their proper utilization. This guidance enhances user safety and the effectiveness of the protective filters.
5. Limitations
It’s important to note that the protective filters discussed in EN 170 are not suitable for direct viewing of intense sources of bright light, such as Xenon high-pressure arc lamps. Additionally, they are not intended for direct or indirect observation of an electric welding arc. These situations require specialized eye protection equipment designed to handle extremely high-intensity light sources.
6. Marking and Numbering
EN 170 references the numbering table for filters and provides guidelines for marking oculars (lenses) and frames of eye protection equipment. Proper marking helps users identify the level of protection and ensures compliance with the standard.
In conclusion, EN 170:2002 is a vital European standard that addresses the protection of the eyes from harmful ultraviolet radiation. It sets out clear requirements for ultraviolet filters and offers guidance on their selection and use. By adhering to EN 170, individuals and employers can ensure that their eye protection equipment provides adequate defense against UV radiation, helping to safeguard eye health in various settings.
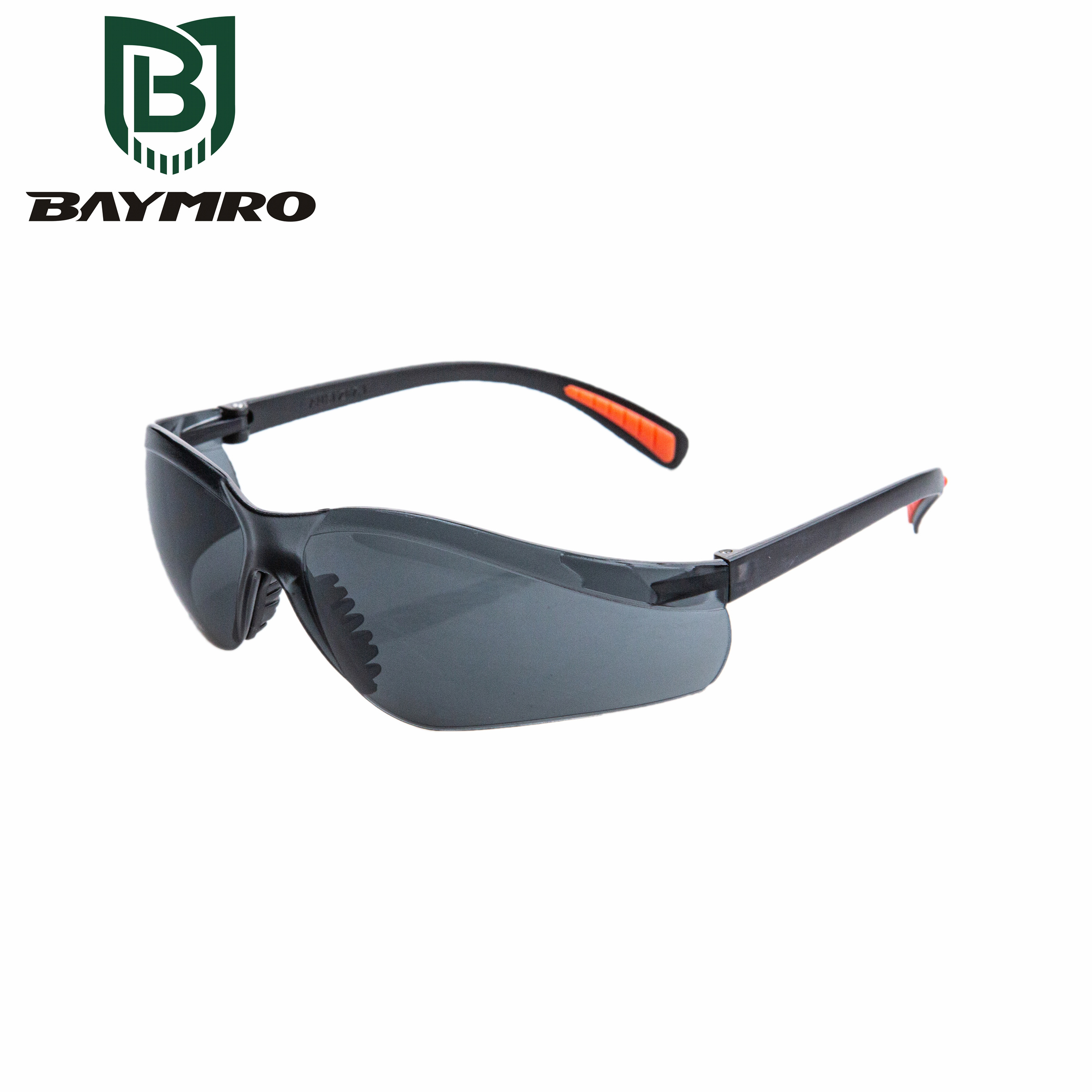

EN 166 is a European standard that pertains to personal eye protection. It specifies the requirements and testing methods for various types of eye protection equipment to ensure their safety and effectiveness. EN 166 is important for ensuring that eye protection devices are suitable for their intended purposes and provide adequate protection against various hazards, including mechanical, chemical, optical, and thermal risks. Let’s break down the key components and aspects of EN 166:
Scope: EN 166 covers a wide range of personal eye protection equipment, including safety glasses, goggles, face shields, welding helmets, and more. It applies to both prescription and non-prescription eyewear.
Classification of Eye Protection: EN 166 classifies eye protection equipment into different categories based on their intended use and the level of protection they provide. The most common classifications include:
- EN 166 F: Basic impact protection for low-energy impacts, such as common industrial activities.
- EN 166 B: Higher impact protection for medium-energy impacts, often used in construction and similar applications.
- EN 166 A: Highest impact protection for high-energy impacts, suitable for more extreme industrial environments.
- EN 166 3: Protection against liquid droplets and splashes.
- EN 166 4: Protection against large dust particles.
- EN 166 5: Protection against gas and fine dust particles.
- EN 166 8: Protection against short circuit electric arcs.
- EN 166 9: Protection against molten metals and hot solids.
- EN 166 K: Resistance to surface damage by fine particles.
Optical Properties: EN 166 also specifies requirements for the optical properties of eye protection equipment, including clarity, distortion, and transmission of light. This ensures that the wearer can see clearly while using the protection.
Frame and Material Requirements: The standard includes guidelines for the materials used in the eyewear, such as frames and lenses, to ensure durability and safety.
Marking and Labeling: Eye protection devices compliant with EN 166 must be marked with relevant symbols and information. These markings indicate the type of protection offered and other essential details, such as the manufacturer’s information.
Testing: EN 166 outlines rigorous testing procedures that eye protection equipment must undergo to ensure their compliance with safety standards. These tests evaluate resistance to impact, penetration, optical quality, and more.
User Instructions: Manufacturers are required to provide clear and comprehensive user instructions to ensure that wearers understand how to properly use and maintain the eye protection equipment.
Compatibility: When applicable, the standard may also specify compatibility requirements with other personal protective equipment (PPE) items, such as respiratory protection.
It’s crucial for employers and individuals to choose eye protection equipment that complies with EN 166 standards to ensure the safety of workers and users in various industrial and hazardous environments. Compliance with these standards helps reduce the risk of eye injuries and ensures that eye protection equipment performs as intended. Keep in mind that while EN 166 is specific to the European Union, similar standards exist in other regions, such as ANSI Z87.1 in the United States.

Introduction
Working with hand-held chainsaws is a task that requires precision, skill, and, most importantly, safety precautions. Chainsaw operators face inherent dangers, and protecting oneself from the risks associated with this equipment is paramount. That’s where standards like EN ISO 11393-4:2019 come into play. This standard, titled “Protective clothing for users of hand-held chainsaws – Part 4: Performance requirements and test methods for protective gloves,” serves as a crucial resource for ensuring the safety of individuals operating chainsaws.
Understanding EN ISO 11393-4:2019
EN ISO 11393-4:2019 is a part of the broader ISO 11393 series, which focuses on protective clothing for users of hand-held chainsaws. Specifically, this standard centers on protective gloves, a vital component of chainsaw operator safety. Chainsaw users face potential hazards, including cuts from the chainsaw chain, making protective gloves an indispensable element of their safety gear.
Performance Requirements
One of the primary functions of EN ISO 11393-4:2019 is to outline performance requirements for protective gloves. These requirements are designed to ensure that gloves effectively shield users from chainsaw-related dangers. The standard specifies the materials, construction, and performance criteria that gloves must meet to provide reliable protection.
Test Methods
To determine whether protective gloves meet the performance requirements, EN ISO 11393-4:2019 provides comprehensive test methods. These tests assess the gloves’ resistance to cutting by chainsaw chains and other relevant performance factors. Rigorous testing ensures that the gloves meet specific safety and protection standards.
Design Specifications
The standard also lays out design specifications for protective gloves. This includes factors such as glove construction, sizing, and ergonomic considerations. Proper design ensures that the gloves are not only protective but also comfortable and functional for the wearer.
Identification and Marking
EN ISO 11393-4:2019 includes guidelines for labeling and marking protective gloves. This is crucial for users to identify gloves that meet the standard’s safety requirements. The markings provide information about the gloves’ protective capabilities and their compliance with the standard.
Annex A: Guidance on Chainsaw Use
Annex A of the standard offers additional guidance on chainsaw use and the selection of gloves. It serves as a valuable resource for chainsaw operators, helping them understand the safe operation of chainsaws while emphasizing the importance of selecting appropriate protective gloves.
Conclusion
Operating hand-held chainsaws is a task that demands precision and safety. EN ISO 11393-4:2019 plays a pivotal role in ensuring the well-being of chainsaw operators. By setting performance requirements, test methods, design specifications, and providing guidance on chainsaw use and glove selection, this standard promotes a safer working environment. Chainsaw operators and stakeholders can rely on EN ISO 11393-4:2019 to make informed choices when it comes to protective gloves, ultimately reducing the risks associated with chainsaw operations and enhancing workplace safety.
 3M
3M Ansell
Ansell Dellta Plus
Dellta Plus Drager
Drager edelrid
edelrid Honeywell
Honeywell JUTEC
JUTEC lakeland
lakeland MSA
MSA New Pig
New Pig Weldas
Weldas