Archive for the ‘Blog’ Category
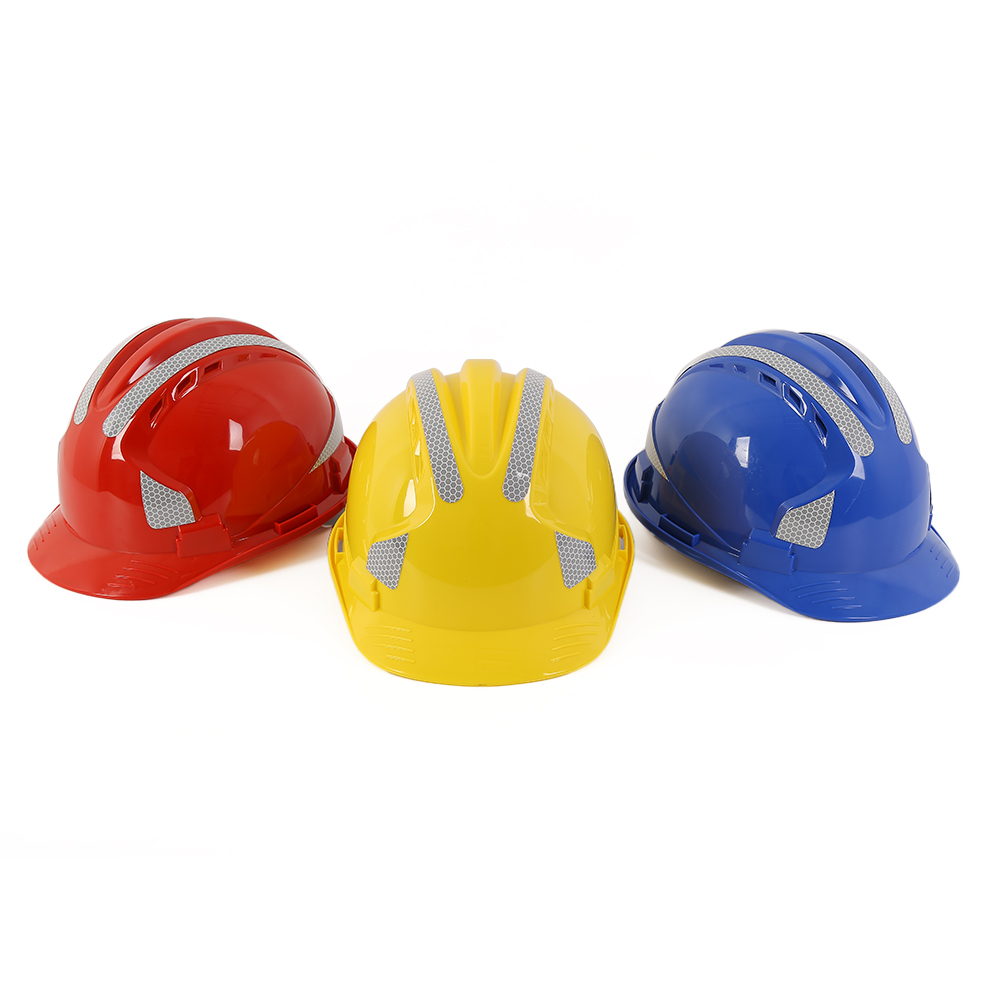

Choosing the right industrial safety helmet is crucial to ensure effective protection in the workplace. Here are some factors to consider when selecting an industrial safety helmet:
Safety Standards:
Ensure that the helmet complies with relevant safety standards and regulations in your region. Standards may vary, but common ones include ANSI/ISEA Z89.1 (USA) or EN 397 (Europe).
Type and Class:
Determine the specific type and class of helmet needed for the job. For example, Class E, G, or C for electrical protection, and Type I or II for impact protection.
Material:
Helmets are typically made of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS). HDPE is lightweight, while ABS provides better impact resistance. Choose a material based on the specific hazards in your workplace.
Suspension System:
The suspension system inside the helmet plays a crucial role in its comfort and impact absorption. Look for a suspension system that can be easily adjusted to provide a secure and comfortable fit.
Ventilation:
Consider the level of ventilation required. Ventilated helmets help to keep the head cool in hot environments. However, if there is a risk of liquid splashes or molten metal, a non-ventilated helmet may be more appropriate.
Accessories:
Some jobs may require additional accessories, such as face shields, earmuffs, or a chin strap. Ensure that the helmet you choose can accommodate the necessary accessories.
Size and Fit:
A properly fitting helmet is essential for effective protection. Helmets are typically available in various sizes, and the suspension system should be adjustable to achieve a secure fit. Conduct a fit test to ensure the helmet sits comfortably on the head without being too tight or too loose.
Weight:
Consider the weight of the helmet, especially if it will be worn for extended periods. A lightweight helmet can reduce strain on the neck and improve overall comfort.
Durability:
Assess the durability of the helmet, considering the demands of the work environment. Helmets should withstand impact, weather conditions, and any chemicals present.
Visibility:
In situations where visibility is critical, such as low-light conditions, consider helmets with high-visibility features, reflective materials, or bright colors.
User Comfort:
The comfort of the user is essential for ensuring that the helmet is worn consistently. Consider features like padded sweatbands and ergonomic design.
Replacement Schedule:
Establish a schedule for replacing helmets regularly, especially if they show signs of wear, damage, or if they have been subjected to a significant impact.
By carefully considering these factors, you can choose an industrial safety helmet that provides the necessary protection for the specific hazards present in your workplace. Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and safety regulations when selecting and using safety helmets.
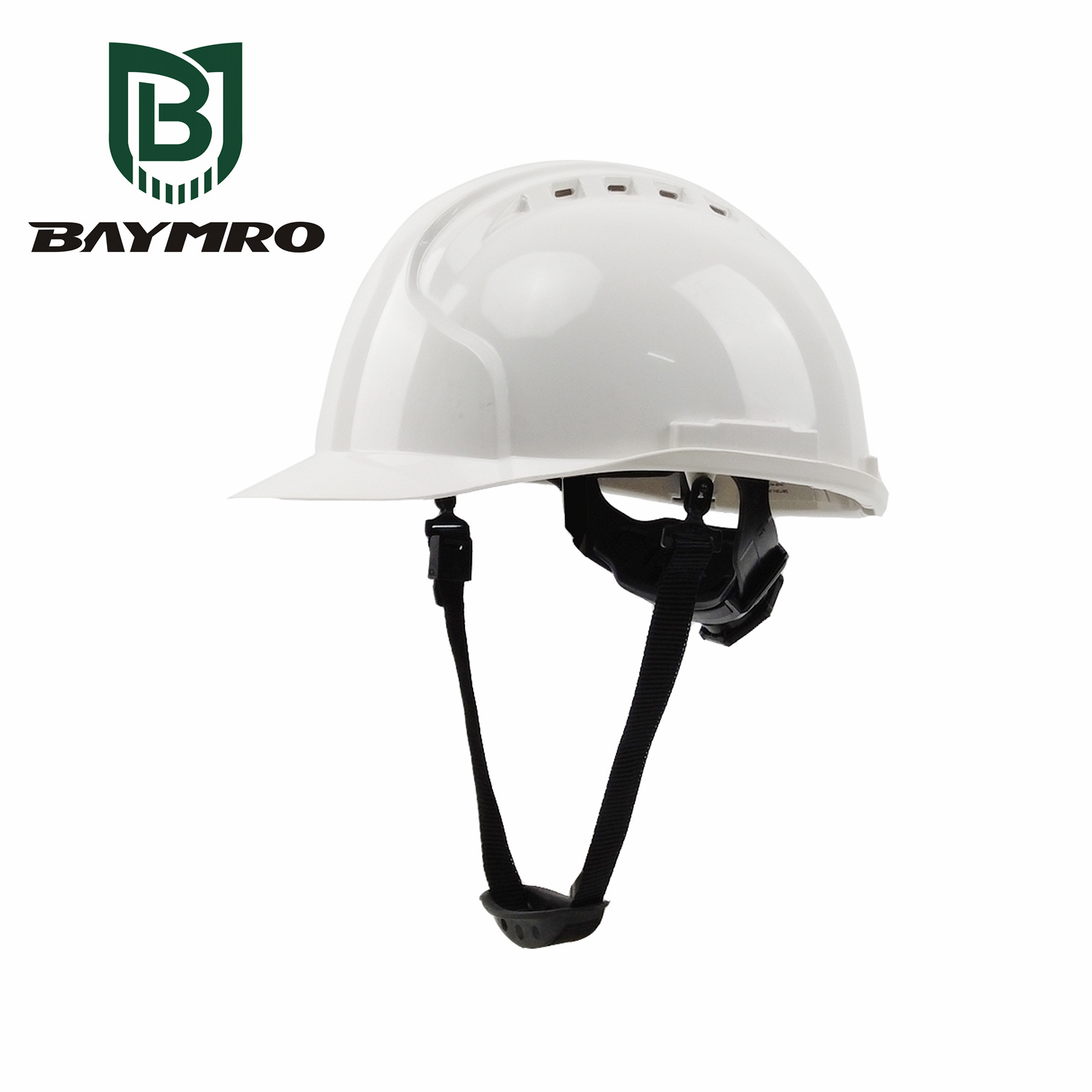

Helmets are essential protective gear in various activities, and their design can significantly impact both safety and comfort. One crucial distinction lies in whether the helmet is ventilated or non-ventilated. Here’s how you can differentiate between the two:
1. Ventilation Structure:
Ventilated Helmets: These helmets are characterized by well-designed ventilation holes or channels, strategically placed to facilitate proper airflow. Ventilation points can be found on the top, sides, or rear of the helmet, aiding in heat dissipation and reducing the temperature inside the helmet for enhanced comfort.
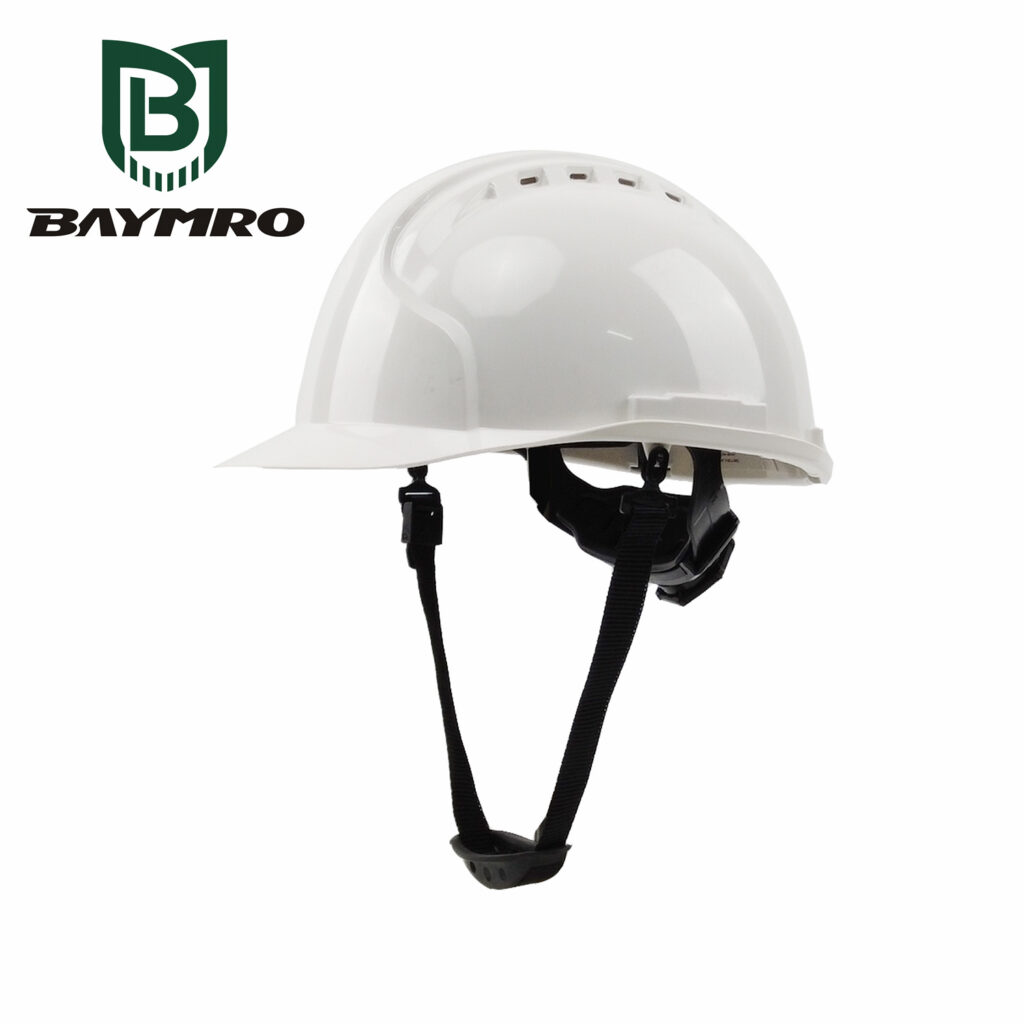

Non-Ventilated Helmets: Conversely, non-ventilated helmets typically lack prominent ventilation holes, focusing more on providing overall head protection. These helmets might be more suitable for colder environments or situations where ventilation is not a primary concern.

2. Comfort:
Ventilated Helmets: Due to their ventilation design, these helmets excel in keeping the wearer’s head cool, especially in hot weather. The airflow helps dissipate heat, minimizing sweat accumulation and improving overall comfort.
Non-Ventilated Helmets: While these helmets prioritize comprehensive head protection, they may lead to a feeling of warmth or discomfort, particularly in hot conditions.
3. Intended Use:
Ventilated Helmets: Ideal for activities or occupations requiring prolonged use in hot environments, such as construction sites or sports events.
Non-Ventilated Helmets: Suited for situations demanding higher overall head protection, such as hazardous construction work or motorcycle riding.
Choosing between a ventilated and non-ventilated helmet depends on your specific needs and the environment in which you’ll be using it. Consider the following factors to make an informed decision:
Environmental Conditions: If you anticipate working or engaging in activities in hot weather, a ventilated helmet may provide better comfort.
Safety Requirements: Jobs or activities with a higher risk of head injuries may necessitate a non-ventilated helmet for maximum protection.
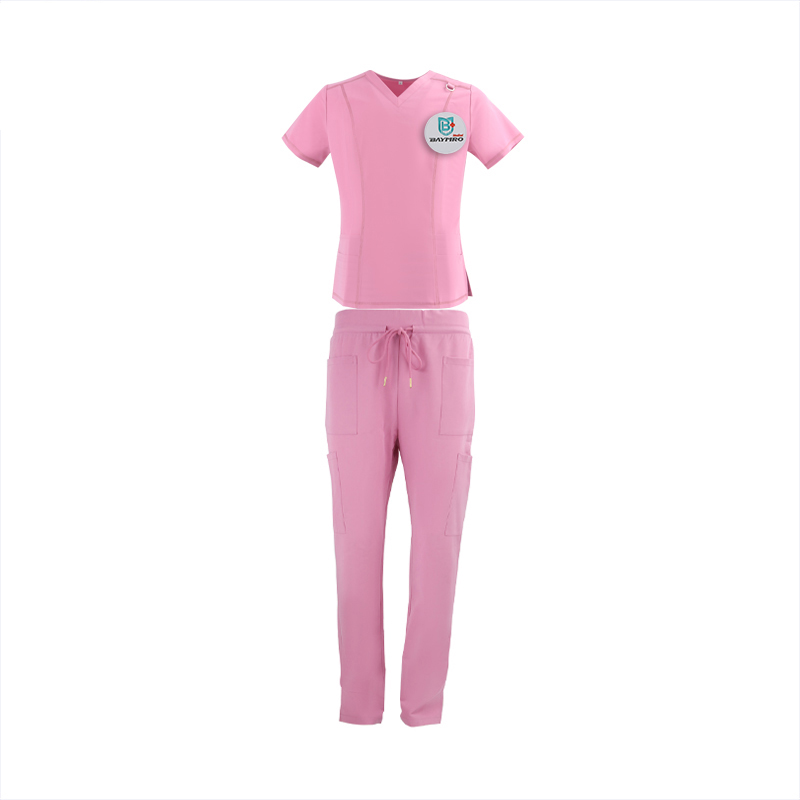

Introduction:
In the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare, the demand for reliable and top-notch medical apparel is paramount. BAYMRO, a distinguished name in the Chinese market, stands out as a leading supplier of medical scrubs, catering to the diverse needs of healthcare professionals globally.
Quality Assurance:
At BAYMRO, we prioritize quality assurance to ensure that our medical scrubs meet and exceed international standards. Our scrubs are crafted from premium materials, blending comfort, durability, and functionality. Whether you’re a medical practitioner, nurse, or part of a healthcare support team, our scrubs are designed to withstand the rigors of the profession while providing unparalleled comfort throughout your demanding workday.
Variety and Customization:
Understanding the varied preferences within the medical community, BAYMRO offers a wide range of medical scrubs in different styles, colors, and sizes. From classic solid colors to contemporary designs, we cater to the diverse tastes of healthcare professionals. Additionally, our customization services allow you to personalize your scrubs with logos, names, and specific color preferences, ensuring a unique and professional appearance.
Innovative Fabric Technology:
BAYMRO prides itself on staying ahead of the curve by incorporating innovative fabric technologies into our medical scrubs. Our scrubs are made from breathable and moisture-wicking fabrics, promoting a comfortable and hygienic environment for medical professionals. The fabrics are also designed to resist stains, ensuring a clean and polished appearance even in the face of challenging situations.
Stringent Quality Control:
To guarantee the highest standards, BAYMRO implements stringent quality control measures at every stage of the manufacturing process. From fabric selection to the final product, our dedicated team of quality control experts ensures that each medical scrub that bears the BAYMRO name is a testament to excellence.
Competitive Pricing and Timely Delivery:
BAYMRO is committed to providing cost-effective solutions without compromising on quality. Our competitive pricing structure makes high-quality medical scrubs accessible to a wide range of healthcare professionals. Furthermore, our efficient logistics and supply chain management ensure timely delivery to our international clients, facilitating a seamless procurement process.
Global Reach:
With a focus on international markets, BAYMRO has established a robust global distribution network. Our medical scrubs are readily available to buyers worldwide, and our customer service team is proficient in catering to the specific requirements of our international clientele.
Conclusion:
When it comes to sourcing premium medical scrubs from China, BAYMRO is the trusted partner for discerning healthcare professionals. With a commitment to quality, customization, and innovation, BAYMRO ensures that medical practitioners around the world are equipped with the finest apparel to excel in their crucial roles. Choose BAYMRO for excellence in medical scrubs and experience the perfect blend of comfort, style, and functionality.

Introduction:
Health, Safety, and Environment (HSE) is a critical aspect of any organization’s operations, regardless of its size or industry. HSE encompasses a wide range of practices, policies, and procedures aimed at safeguarding the well-being of employees, protecting the environment, and ensuring the overall sustainability of the business. This guide provides an overview of HSE principles, practices, and how to implement them effectively.

Section 1: Understanding HSE
1.1. What is HSE?
HSE refers to a holistic approach to managing health, safety, and environmental risks within an organization. It involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks to prevent accidents, injuries, illnesses, and environmental harm.
1.2. Why is HSE Important?
HSE is crucial for several reasons:
Protecting human life and well-being.
Reducing accidents and associated costs.
Complying with legal and regulatory requirements.
Enhancing an organization’s reputation.
Demonstrating social responsibility.
Reducing environmental impact.
Section 2: Core Components of HSE
2.1. Health (H):
Occupational health: Promoting employee health, including physical and mental well-being.
Health assessments: Regular check-ups and risk assessments for employees.
Health promotion: Encouraging a healthy lifestyle and providing wellness programs.
2.2. Safety (S):
Hazard identification and risk assessment: Identifying potential workplace hazards and assessing their risks.
Safety procedures: Developing and implementing safety protocols, including emergency response plans.
Training: Providing safety training to employees at all levels.
Incident reporting and investigation: Establishing a system for reporting, investigating, and learning from incidents.
2.3. Environment (E):
Environmental impact assessments: Evaluating the impact of operations on the environment.
Environmental management systems (EMS): Implementing and maintaining systems to control and reduce environmental impacts.
Compliance with environmental laws and regulations: Ensuring that the organization adheres to all applicable laws.
Sustainability initiatives: Promoting sustainable practices and reducing resource consumption.
Section 3: Implementing an HSE Program
3.1. HSE Policy:
Develop a clear and comprehensive HSE policy that outlines the organization’s commitment to health, safety, and the environment.
Communicate the policy to all employees and stakeholders.
3.2. HSE Management System:
Establish a structured system for managing HSE, such as ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety Management Systems) and ISO 14001 (Environmental Management Systems).
Define responsibilities and accountabilities within the system.
3.3. Risk Assessment:
Identify potential risks to health, safety, and the environment.
Prioritize risks based on severity and likelihood.
Develop strategies to mitigate or eliminate risks.
3.4. Training and Awareness:
Provide HSE training for all employees.
Ensure that employees understand their roles and responsibilities in maintaining HSE standards.
3.5. Incident Management:
Establish clear procedures for reporting and investigating incidents.
Use incident data to identify trends and implement preventive measures.
3.6. Emergency Preparedness:
Develop and regularly test emergency response plans.
Ensure employees are familiar with emergency procedures.
Section 4: Monitoring and Continuous Improvement
4.1. Performance Metrics:
Define key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure HSE performance.
Regularly collect and analyze data to evaluate progress.
4.2. Audits and Inspections:
Conduct regular internal and external audits to assess compliance and effectiveness.
Address non-conformities and implement corrective actions.
4.3. Feedback and Communication:
Encourage employees to provide feedback and suggestions for HSE improvements.
Communicate HSE successes and challenges throughout the organization.
4.4. Continuous Improvement:
Use data and feedback to identify areas for improvement.
Update policies and procedures as needed to enhance HSE performance.
Section 5: Legal and Regulatory Compliance
5.1. Stay Informed:
Stay up to date with relevant laws and regulations.
Monitor changes and adapt policies and procedures accordingly.
5.2. Compliance Reporting:
Ensure timely and accurate reporting to relevant authorities.
Maintain records of compliance-related activities.
Section 6: Conclusion
Implementing a robust HSE program is essential for the well-being of employees, the preservation of the environment, and the overall success of an organization. By prioritizing health, safety, and environmental protection, businesses can mitigate risks, reduce costs, enhance their reputation, and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Remember that HSE is an ongoing commitment that requires regular assessment, adaptation, and improvement. Continuous vigilance and a strong organizational culture of safety and responsibility are essential for achieving and maintaining HSE excellence.
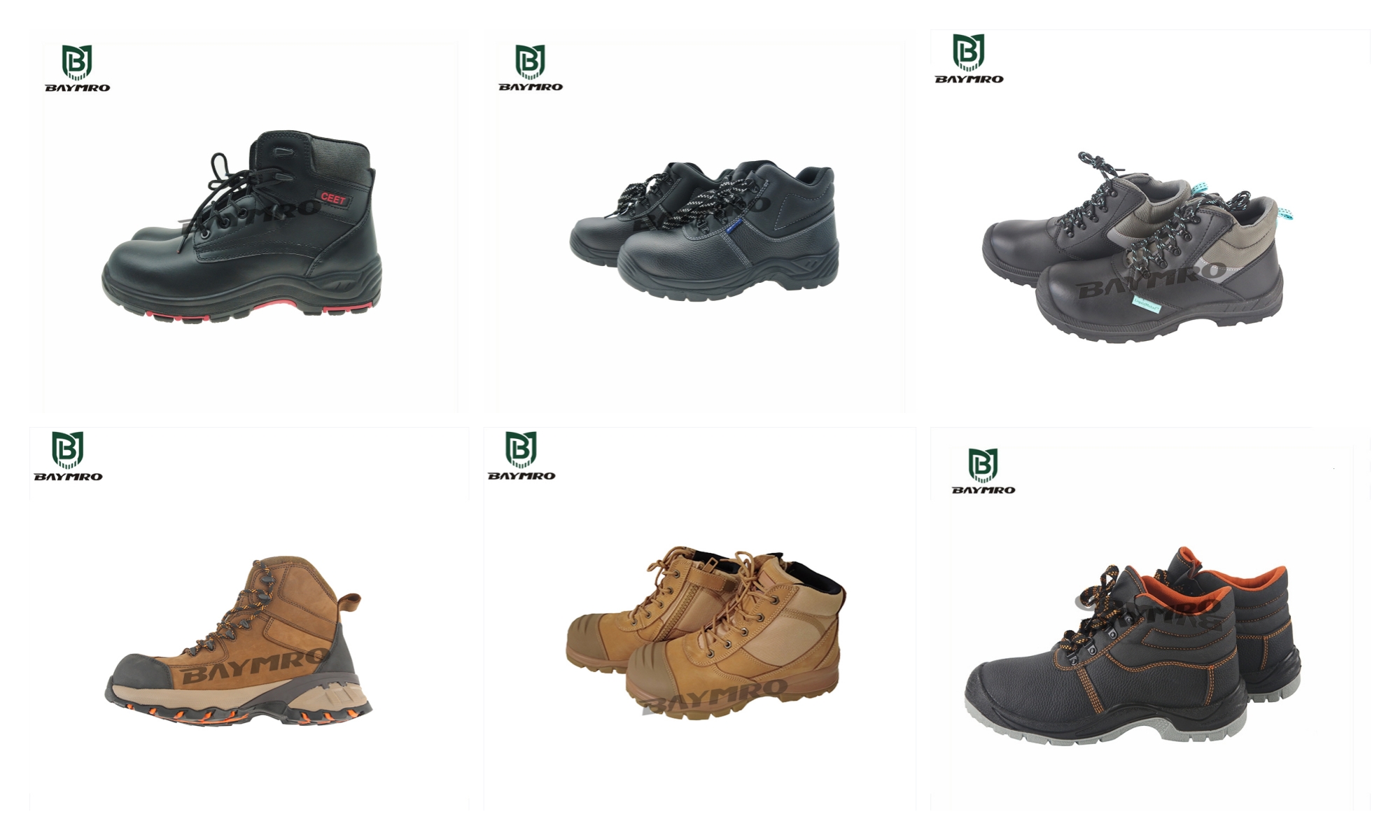

Construction sites are dynamic, challenging environments where a myriad of hazards can threaten the well-being of workers. Safety shoes are a crucial part of personal protective equipment (PPE) that can mitigate these risks, offering protection for one of the most vulnerable parts of the body: the feet. In this article, we’ll explore the factors you should consider when selecting the right safety shoes for construction sites.

Toe Protection: Steel or Composite?
The first and foremost feature to consider in safety shoes is toe protection. Falling objects, heavy equipment, and compression hazards are common on construction sites. Steel toe caps are a traditional choice, offering robust protection. However, composite toe caps have gained popularity due to their lightweight and non-conductive properties, making them suitable for those working near electrical hazards. Choose the type of toe protection that aligns with your specific job requirements.
Slip Resistance
Construction sites are often rife with slippery surfaces, especially in wet or muddy conditions. Slip-resistant outsoles are essential to prevent accidents. Look for shoes with tread patterns designed for grip on a variety of surfaces. ASTM F2413-18, the standard for performance requirements for protective (safety) toe cap footwear, has specific guidelines for slip resistance.
Puncture Resistance
Sharp objects like nails, screws, or debris can pose a puncture risk to your feet. Safety shoes with puncture-resistant midsoles provide an additional layer of protection. These midsoles are often made of materials like Kevlar or steel and can significantly reduce the risk of injury.
Electrical Hazard (EH) Protection
If your work involves electricity, whether directly or indirectly, EH-rated safety shoes are crucial. These shoes are designed to reduce the risk of electrical shock. They feature special insulating materials and construction that prevent electrical currents from passing through the sole into the wearer’s body.
Waterproof and Weatherproof Features
Construction sites are open to the elements, and workers often find themselves dealing with rain, mud, or snow. Waterproof or weatherproof safety shoes keep your feet dry and comfortable, reducing the risk of cold-related injuries. Look for shoes made with waterproof membranes and sealed seams to ensure complete protection.
Ankle Support
High-top or mid-top safety boots can provide additional ankle support and protection, which can be invaluable when navigating uneven terrain or carrying heavy loads. These boots offer stability and reduce the risk of ankle injuries.
Comfort and Fit
Comfort and proper fit are essential for long hours of work. Ill-fitting or uncomfortable safety shoes can lead to fatigue, blisters, and reduced productivity. Make sure your shoes fit well, provide adequate arch support, and have cushioning for comfort. Many brands offer various width options to accommodate different foot shapes.
Durability
Construction work is tough on footwear. Look for safety shoes made from high-quality materials and construction techniques. A durable shoe will not only protect your feet but also last longer, saving you money in the long run.
Insulation
If you work in cold conditions, insulated safety shoes are a must. They help keep your feet warm, ensuring comfort and preventing cold-related injuries. Insulated safety shoes are designed to trap heat and maintain a comfortable temperature.
Weight
Consider the weight of your safety shoes. If you need to move quickly or frequently climb ladders, lighter safety shoes may be more practical. Balance weight with other protective features to find the right combination for your needs.
Compliance
Ensure that the safety shoes you choose meet the relevant safety standards in your region. For example, in the United States and Canada, safety shoes are subject to standards set by ASTM, ANSI, and CSA. Compliant shoes have been tested to meet specific performance criteria.
In conclusion, choosing the right safety shoes for construction sites is a critical decision that directly impacts your safety and comfort. Assess the specific hazards and working conditions on your construction site, and select safety shoes that offer the necessary protection. Regularly inspect and maintain your safety shoes to ensure they continue to perform effectively and protect your feet throughout your demanding workdays. Prioritize safety, and invest in quality safety shoes to safeguard your most valuable assets—your feet.
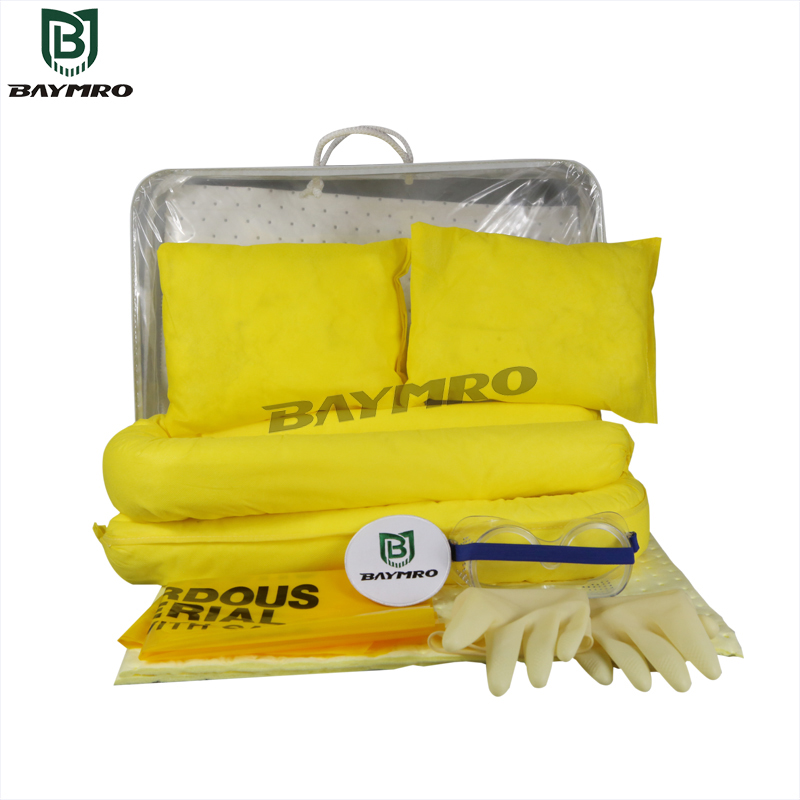

Oil-absorbing cotton, a remarkable material, plays a pivotal role in managing oil spills and controlling oil-based pollutants. This versatile substance is designed to soak up oils and hydrocarbons while repelling water. In this article, we’ll explore how oil-absorbing cotton is made, provide an overview of various adsorbent materials, discuss its extensive range of applications, and consider alternative industrial adsorption materials.
1.How is oil-absorbing cotton made?
- Oil-absorbing cotton is typically produced using hydrophobic materials that have a natural affinity for oils and hydrocarbons while repelling water. Here’s a basic overview of the manufacturing process:
- Material Selection: The primary material used in oil-absorbing cotton is often synthetic, like polypropylene. Polypropylene is cost-effective and efficient at absorbing and retaining oils. Natural materials like cellulose, derived from wood pulp, are also used in some cases, offering a biodegradable and eco-friendly option.
- Fiber Formation: The selected material is processed into fibers that are layered to create a pad or mat. These fibers create a porous structure that allows for efficient absorption of oil.
- Hydrophobic Treatment: Many oil-absorbing cotton products are treated with hydrophobic chemicals or coatings to enhance their oil-absorption capabilities further.
2.Brief Description of Adsorbent Materials
Adsorbent materials can be broadly categorized into three series:
- Oil Absorbent Materials: These materials are specifically designed to absorb oils and hydrocarbons. Oil-absorbing cotton is a prime example, excelling at this task.
- Chemical Adsorbent Material Series: These materials are engineered to absorb a wide range of chemicals and hazardous substances. They are crucial in industrial settings where chemical spills are a concern.
- General Adsorbent Material Series: These materials are versatile and can absorb a variety of liquids, including water, oils, and chemicals. They are commonly used in spill response kits and everyday industrial cleanup.
3.What are the uses of oil-absorbing cotton?
- Oil-absorbing cotton finds a wide range of applications across various industries:
- Environmental Cleanup: Oil-absorbing cotton is crucial for managing oil spills in bodies of water, ensuring that the oil is contained and absorbed without further contaminating the environment.
- Industrial Settings: In manufacturing and industrial facilities, these materials are used to control and clean up oil-based spills that can occur during processes or machinery maintenance.
- Garages and Workshops: Automotive repair shops and garages utilize oil-absorbing cotton to absorb and dispose of oil and fuel spills to maintain a clean and safe working environment.
- Spill Response Kits: Oil-absorbing cotton is an integral component of spill response kits, providing a quick and effective solution for containing and absorbing accidental oil or chemical spills.
4.What are the options for industrial adsorption materials?
In addition to oil-absorbing cotton, there are several other industrial adsorption materials available:
- Oil-Absorbing Rolls: These are long, continuous rolls of oil-absorbent material that can be used to cover larger surface areas and absorb oil or chemical spills efficiently.
- Oil-Absorbing Grids: Grids are often used in marine settings to contain and absorb oil spills on the water’s surface. They are designed to float and trap oil effectively.
- Oil-Absorbing Kits: Spill response kits typically include a combination of materials such as oil-absorbing pads, rolls, socks, and protective gear. These kits are comprehensive solutions for managing spills of various sizes.
In conclusion, oil-absorbing cotton is a crucial tool for managing oil-based spills and maintaining a clean and safe environment in a variety of industries. Understanding its manufacturing process, the different categories of adsorbent materials, and the various options for industrial adsorption materials helps emphasize the importance of selecting the right material for each specific application, from small workshop accidents to large-scale oil spills on water bodies. This versatility ensures that there is a solution for every spill scenario, promoting environmental sustainability and workplace safety.
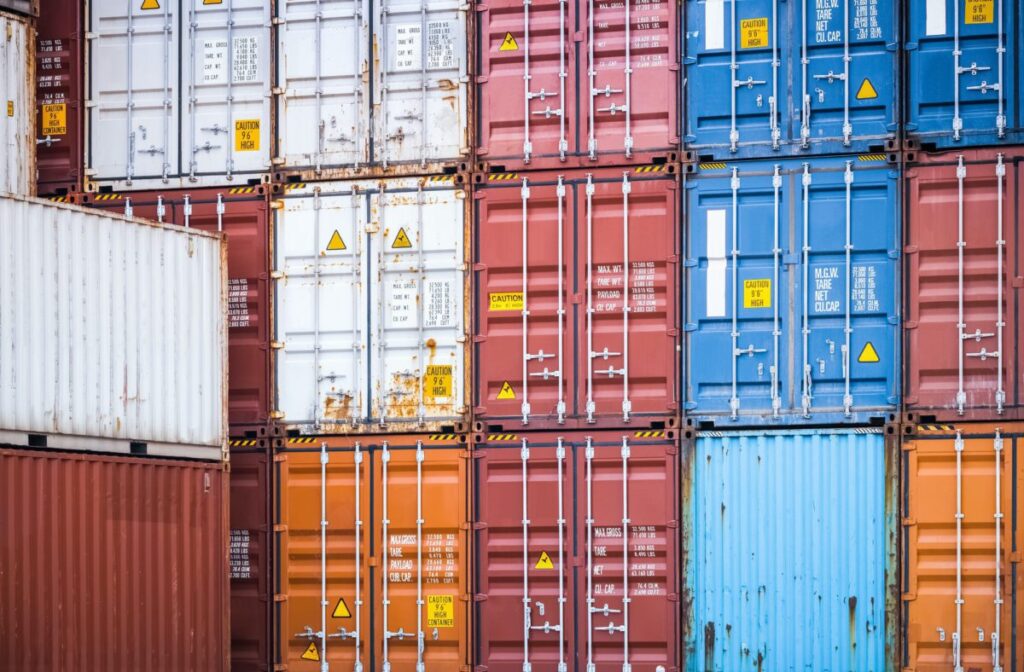

Introduction
In our increasingly interconnected world, the efficient movement of goods is pivotal to global trade and the functioning of our modern society. At the heart of this logistical marvel are cargo containers, the unsung heroes that quietly revolutionized the way we transport goods. In this article, we’ll explore the fascinating world of cargo containers, their history, types, importance, and their impact on global commerce.
The History of Cargo Containers
The concept of containerized cargo isn’t new, but the system we use today was developed in the mid-20th century. The American entrepreneur Malcolm McLean is often credited with the innovation. In 1956, he introduced the first standardized cargo container, a 33-foot-long steel box that could be loaded onto ships, trains, and trucks without unloading its contents. This sparked a revolution in the shipping industry, making it possible to efficiently transport goods from factories to ports, across oceans, and all the way to your local store shelves.
Types of Cargo Containers
Today, cargo containers come in various sizes and types, each designed for specific cargo and transportation needs. The most common types include:
Standard Dry Containers: These are the iconic rectangular steel boxes used for most general cargo, from electronics to clothing. They come in 20-foot and 40-foot lengths.
Refrigerated Containers: Known as “reefers,” these containers are equipped with cooling systems and are crucial for transporting perishable goods like fruits, vegetables, and pharmaceuticals.
Flat Rack Containers: These have collapsible sides and no roof, making them ideal for oversized cargo like machinery and heavy equipment.
Open-Top Containers: They lack a solid roof and are used for tall or bulky cargo that can’t fit into standard containers, such as construction materials.
Tank Containers: Designed to transport liquids, chemicals, or gases, these containers have cylindrical tanks made of stainless steel.
The Importance of Cargo Containers
Efficiency: Cargo containers have streamlined the entire logistics process. The standardized sizes mean that loading and unloading is a breeze, reducing turnaround times at ports and terminals.
Security: Once sealed, cargo containers are extremely secure, making it difficult for unauthorized access or tampering. This has significantly reduced pilferage during transportation.
Protection: Cargo containers protect goods from the elements, ensuring that they arrive in the same condition as when they were loaded.
Global Trade: Without cargo containers, the rapid growth of international trade and the global supply chain wouldn’t be possible. They have driven globalization and increased access to products from all over the world.
Environmental Impact: Containerization has led to more efficient transport systems, which in turn has had a positive impact on reducing transportation-related emissions and energy consumption.
The Impact on Global Commerce
The rise of cargo containers has had a profound effect on the world economy. They’ve made it possible for businesses to tap into a global market and have enabled just-in-time inventory practices that minimize holding costs. Some key impacts include:
Lower Costs: The efficiency of containerization has significantly reduced transportation costs, enabling more affordable goods for consumers.
Market Access: Smaller businesses can now participate in international trade, leveling the playing field and promoting competition.
Supply Chain Integration: Cargo containers have led to a more integrated global supply chain, allowing for more efficient production and distribution processes.
Economic Growth: Ports and logistics hubs have sprung up around the world, driving economic development in many regions.
Conclusion
Cargo containers are often overlooked, yet they are the lifeblood of global trade and commerce. These simple, standardized boxes have transformed the world of logistics, making it possible for goods to traverse the globe efficiently and affordably. As we continue to navigate the complexities of an interconnected world, let us not forget the unassuming cargo container and its crucial role in shaping the way we live, consume, and do business on a global scale.
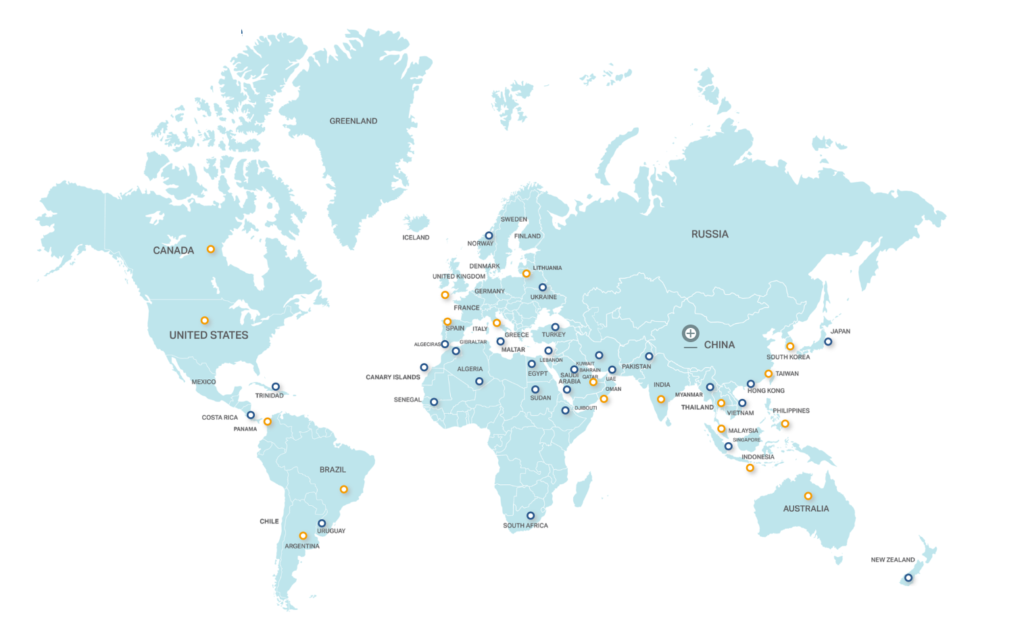
The world has numerous important ports that play a critical role in facilitating global trade and commerce. These ports vary in terms of their size, capacity, and specialization. Here are some of the most significant and strategically important ports from various regions of the world:
- Port of Shanghai – Shanghai, China
- Port of Singapore – Singapore
- Port of Shenzhen – Shenzhen, China
- Port of Ningbo-Zhoushan – Zhejiang, China
- Port of Guangzhou – Guangzhou, China
- Port of Busan – Busan, South Korea
- Port of Hong Kong – Hong Kong
- Port of Qingdao – Qingdao, China
- Port of Rotterdam – Rotterdam, Netherlands
- Port of Antwerp – Antwerp, Belgium
- Port of Hamburg – Hamburg, Germany
- Port of Los Angeles – Los Angeles, USA
- Port of Long Beach – Long Beach, USA
- Port of New York and New Jersey – New York/New Jersey, USA
- Port of Houston – Houston, USA
- Port of Savannah – Savannah, USA
- Port of Charleston – Charleston, USA
- Port of Miami – Miami, USA
- Port of New Orleans – New Orleans, USA
- Port of Vancouver – Vancouver, Canada
- Port of Montreal – Montreal, Canada
- Port of Sydney – Sydney, Australia
- Port of Melbourne – Melbourne, Australia
- Port of Brisbane – Brisbane, Australia
- Port of Tokyo – Tokyo, Japan
- Port of Yokohama – Yokohama, Japan
- Port of Osaka – Osaka, Japan
- Port of Kobe – Kobe, Japan
- Port of Dubai – Dubai, United Arab Emirates
- Port of Jebel Ali – Jebel Ali, United Arab Emirates
- Port of Colombo – Colombo, Sri Lanka
- Port of Mumbai – Mumbai, India
- Port of Chennai – Chennai, India
- Port of Nhava Sheva – Mumbai, India
- Port of Durban – Durban, South Africa
- Port of Cape Town – Cape Town, South Africa
- Port of Alexandria – Alexandria, Egypt
- Port of Suez – Suez, Egypt
- Port of Barcelona – Barcelona, Spain
- Port of Valencia – Valencia, Spain
- Port of Genoa – Genoa, Italy
- Port of Marseille – Marseille, France
- Port of Le Havre – Le Havre, France
- Port of Hamburg – Hamburg, Germany
- Port of Felixstowe – Felixstowe, United Kingdom
- Port of Southampton – Southampton, United Kingdom
- Port of Liverpool – Liverpool, United Kingdom
- Port of Istanbul – Istanbul, Turkey
- Port of Novorossiysk – Novorossiysk, Russia
- Port of Vladivostok – Vladivostok, Russia
Please note that these are just a selection of major ports around the world, and there are many more ports in various countries handling international trade and commerce.
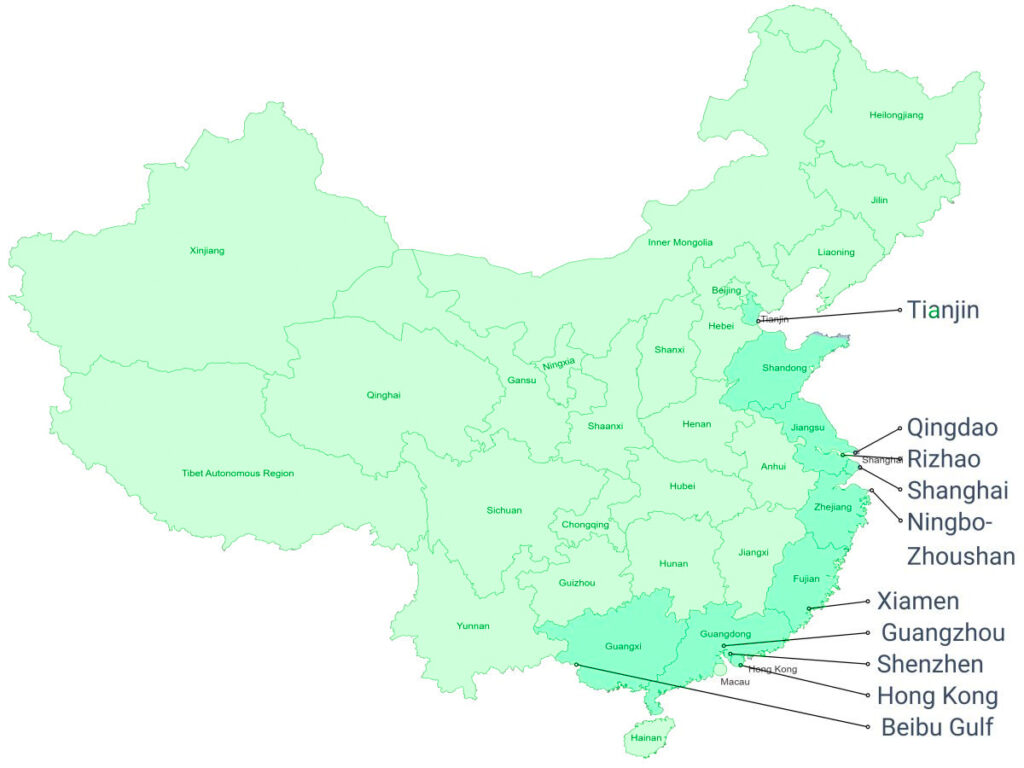
China has a vast network of ports due to its extensive coastline and strategic importance in global trade. Here are some notable ports in different regions of China:
Northern China:
Tianjin Port: Located in Tianjin, it is one of the largest and busiest ports in northern China, handling containers, bulk cargo, and liquid bulk cargo.
Qinhuangdao Port: Situated in Hebei province, it specializes in handling coal and bulk cargo.
Dalian Port: Located in Liaoning province, Dalian is a major port in northeast China, dealing with containers, bulk cargo, and oil shipments.
Eastern China:
Shanghai Port: The largest and busiest port in China, situated in Shanghai, it handles a wide range of cargo, including containers, bulk cargo, and oil.
Ningbo-Zhoushan Port: Located in Zhejiang province, it is one of the world’s largest container ports and handles various types of cargo.
Qingdao Port: Located in Shandong province, Qingdao Port handles containers, bulk cargo, and crude oil.
Lianyungang Port: Found in Jiangsu province, Lianyungang Port is essential for trade with East Asian countries.
Southern China:
Shenzhen Port: Comprising Yantian Port, Shekou Port, and Chiwan Port, it is a major hub for foreign trade and one of the most significant container ports in China.
Guangzhou Port: Located in Guangdong province, along with Huangpu Port, it handles a substantial amount of cargo in southern China.
Xiamen Port: Situated in Fujian province, Xiamen Port specializes in container and general cargo handling.
Hong Kong and Macau:
Hong Kong Port: Although not part of mainland China, Hong Kong’s port is a crucial transshipment hub and plays a significant role in China’s trade.
Macau Port: While Macau is primarily known for its tourism and entertainment industry, it also has a port that handles cargo.
These are just a few examples of the many ports in China. China’s extensive port infrastructure is vital for its import and export activities, contributing significantly to its economic growth and its role in global trade.


Choosing the right hearing protection products is crucial to safeguard your hearing in noisy environments. The choice depends on several factors, including the noise level, your specific needs, comfort, and the environment. Here are steps to help you select appropriate hearing protection:
Assess Noise Levels:
Determine the noise level in your workplace or environment. You may need a professional noise assessment to accurately measure sound levels. This will help you understand the level of protection required.
Understand Types of Hearing Protection:
Familiarize yourself with different types of hearing protection products:
Earplugs: Small, insertable devices that go inside the ear canal.
Earmuffs: Head-worn devices that cover the ears.
Level-Dependent Hearing Protectors: Earmuffs or earplugs that adjust protection based on noise levels.
Communication Hearing Protectors: Allow for communication while providing protection.
Consider Noise Reduction Rating (NRR):
Look for the Noise Reduction Rating (NRR) when choosing earplugs or earmuffs. The NRR indicates the level of noise reduction provided by the product. Select a product with an NRR appropriate for your noise environment.
Fit and Comfort:
Ensure a proper fit. Ill-fitting hearing protection may not provide the expected noise reduction. Try different sizes and types to find the most comfortable fit.
Comfort is essential for extended use. Choose products that you can wear comfortably throughout your work shift.
Communication Needs:
If you need to communicate while wearing hearing protection, consider products with built-in communication features or those that allow for easy removal or adjustment.
Durability and Maintenance:
Consider the durability of the product, especially if you work in harsh environments. Some hearing protection devices are more robust than others.
Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for cleaning and maintenance to ensure longevity and effectiveness.
Environmental Factors:
Consider environmental factors like heat, humidity, and dust when selecting hearing protection. Some products may be better suited for specific conditions.
Training and Education:
Provide training and education to workers on the proper use of hearing protection. Ensure they know how to fit, wear, and maintain their hearing protection devices.
Regulatory Compliance:
Ensure that the selected hearing protection products comply with local regulations and standards, such as ANSI S3.19 in the United States or EN 352 in Europe.
Regular Testing:
Periodically assess the effectiveness of the chosen hearing protection through noise monitoring and hearing tests to ensure it provides adequate protection.
Consult with Experts:
If you are unsure about which hearing protection products are suitable for your specific needs, consider consulting with occupational health and safety professionals or audiologists who can provide guidance.
Remember that hearing protection is a crucial aspect of workplace safety. Choosing the right products and using them correctly can help prevent noise-induced hearing loss and protect your long-term hearing health.
 3M
3M Ansell
Ansell Dellta Plus
Dellta Plus Drager
Drager edelrid
edelrid Honeywell
Honeywell JUTEC
JUTEC lakeland
lakeland MSA
MSA New Pig
New Pig Weldas
Weldas