Archive for the ‘Certification’ Category
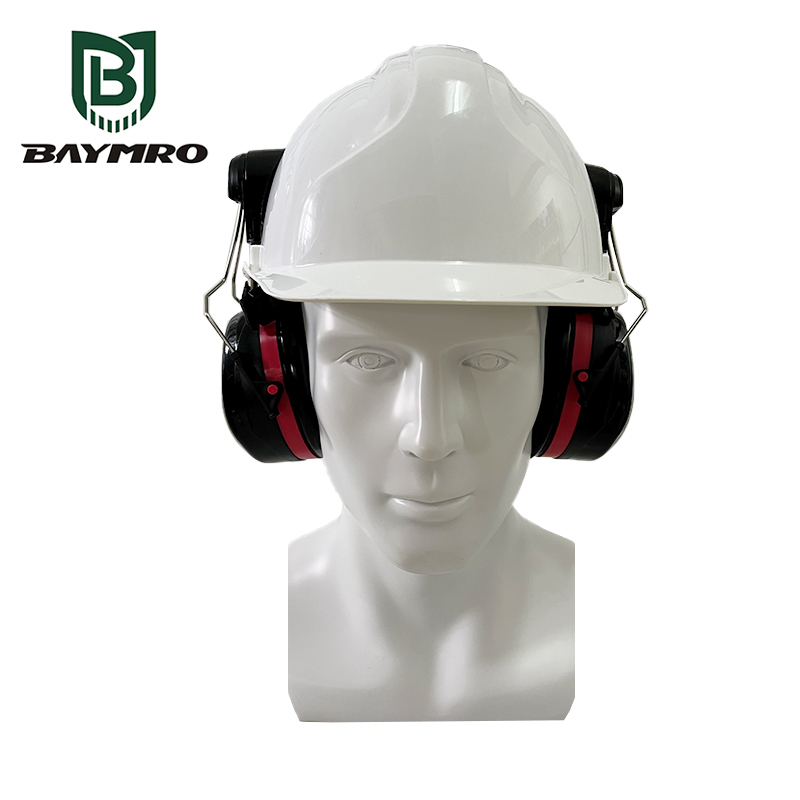

EN 352 is a set of European standards that specify requirements and testing methods for various types of hearing protection devices (HPDs) used in occupational and recreational settings. These standards are designed to ensure the effectiveness and safety of hearing protection products and to provide a common framework for manufacturers, regulatory bodies, and users across Europe. EN 352 standards cover a range of hearing protection devices, including earplugs, earmuffs, and ear canal caps.
Here is an overview of some key aspects of EN 352:
EN 352-1: Earmuffs
This part of the standard covers the requirements for earmuffs. It specifies criteria for noise reduction, comfort, and durability. Earmuffs are typically designed to cover the entire ear and are held in place by a headband.
EN 352-2: Earplugs
EN 352-2 outlines the requirements for earplugs, which are small devices designed to be inserted into the ear canal. This standard addresses aspects such as noise reduction, fit, and comfort.
EN 352-3: Earmuffs attached to an industrial safety helmet
This part of the standard focuses on earmuffs that are integrated into industrial safety helmets. It defines requirements for the combination of hearing protection and head protection.
EN 352-4: Level-dependent earmuffs
Level-dependent earmuffs are designed to protect the user from high-level noise while allowing them to hear lower-level sounds, such as speech or warning signals. This standard sets requirements and performance criteria for such devices.
EN 352-5: Active noise reduction earmuffs
Active noise reduction (ANR) earmuffs use electronic technology to cancel out or reduce noise. EN 352-5 specifies requirements and test methods for ANR earmuffs.
EN 352-6: Earmuffs with electrical audio input
Earmuffs with electrical audio input allow users to listen to external audio sources while providing hearing protection. This standard outlines requirements and testing procedures for these devices.
EN 352-7: Level-dependent earplugs
Similar to level-dependent earmuffs, level-dependent earplugs offer variable protection based on noise levels. EN 352-7 covers the requirements and testing methods for these types of earplugs.
EN 352-8: Entertainment audio earplugs
This standard is for earplugs designed for recreational or entertainment purposes, such as concerts or clubbing. It addresses requirements for noise reduction and sound quality.
EN 352-9: Earmuffs with active noise reduction
EN 352-9 focuses on earmuffs equipped with active noise reduction technology and specifies requirements for these products.
It’s essential for manufacturers to conform to these standards when designing and producing hearing protection devices. Additionally, employers and users should select and use hearing protection that complies with these standards to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the hearing protection measures in various noisy environments. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper fitting and usage of hearing protection devices to protect your hearing effectively.


In the world of workplace safety, the protection of the head is paramount. When it comes to safeguarding the heads of workers from a myriad of occupational hazards, ANSI Z89.1 stands as a beacon of safety standards. ANSI Z89.1, developed by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI), is a critical standard that sets the requirements for industrial head protection, specifically hard hats and safety helmets. In this article, we will explore the significance of ANSI Z89.1 and its role in ensuring workplace safety.
1. Purpose and Scope
ANSI Z89.1 is a comprehensive standard that focuses on head protection equipment used in various industries and occupational settings. The primary purpose of this standard is to establish a consistent framework for the design, testing, and performance of hard hats and safety helmets. These protective helmets are essential for safeguarding the heads of workers in environments where head injuries may occur due to falling objects, impact, electrical hazards, or other potential dangers.
2. Types of Protection
ANSI Z89.1 covers a wide range of protective headgear, including:
Type I Helmets: Designed to provide protection to the top of the head, they are commonly used in situations where falling objects are a risk.
Type II Helmets: Offering protection both to the top and sides of the head, they are suitable for environments where lateral impact is a concern.
3. Design Requirements
The standard outlines stringent design requirements for hard hats and safety helmets. These requirements ensure that the headgear provides effective protection while also being comfortable and practical for extended wear. Design factors include impact resistance, shock absorption, electrical insulation, and suspension systems.
4. Testing Procedures
Helmets that comply with ANSI Z89.1 must undergo rigorous testing procedures to verify their compliance with the standard. These tests evaluate various aspects of performance, including impact resistance, electrical insulation properties, and suspension system effectiveness.
5. Marking and Labeling
Products that meet the ANSI Z89.1 standard are marked and labeled accordingly. These markings include information about the manufacturer, product model, and compliance with the standard. Users can refer to these markings to ensure they are selecting suitable headgear for their specific workplace needs.
6. Workplace Safety
ANSI Z89.1 compliant hard hats and safety helmets are essential for maintaining workplace safety in various industries, including construction, manufacturing, and utilities. Employers are often required to provide and enforce the use of ANSI-compliant head protection to reduce the risk of head injuries in hazardous work environments.
7. Compatibility
ANSI Z89.1 is compatible with other workplace safety standards and regulations, ensuring that head protection can be integrated seamlessly into broader safety protocols and personal protective equipment (PPE) requirements.
In summary, ANSI Z89.1 is a critical American standard that sets the benchmark for the design, testing, and performance of hard hats and safety helmets used in a variety of work environments. Compliance with this standard is essential for ensuring the safety and well-being of workers who face the risk of head injuries due to occupational hazards. ANSI Z89.1 underscores the importance of comprehensive safety measures in the workplace and serves as a vital component of occupational safety and health programs.

EN 397 is a European standard that sets forth the specifications and requirements for industrial safety helmets. These helmets are essential protective gear designed to safeguard the heads of workers in various industrial and occupational settings across Europe. EN 397 ensures that safety helmets meet stringent criteria for design, testing, and performance. Here’s an overview of EN 397:
1. Purpose and Scope
EN 397 primarily focuses on safety helmets used to protect the heads of individuals working in industries and occupations where head injuries may occur. The standard aims to establish a consistent framework for the design, testing, and performance of industrial safety helmets.
2. Types of Protection
This standard covers a range of protective headgear, including hard hats and safety helmets. These helmets are designed to safeguard the head against different types of risks commonly encountered in industrial, construction, and similar work environments.
3. Design Requirements
EN 397 outlines design requirements for industrial safety helmets, ensuring they provide comprehensive protection while also being comfortable and user-friendly. These requirements encompass factors such as impact resistance, shock absorption, and chin strap performance.
4. Testing Procedures
Safety helmets that comply with EN 397 must undergo rigorous testing procedures to verify their compliance with the standard. These tests evaluate various aspects of performance, including impact resistance, penetration resistance, and resistance to flame.
5. Marking and Labeling
Products that meet the EN 397 standard must be marked and labeled accordingly. These markings typically include information about the manufacturer, product model, and compliance with the standard. Such markings help users identify suitable headgear for their specific needs.
6. Workplace Safety
Compliance with EN 397 is essential for maintaining workplace safety in Europe. Employers are often required to provide and enforce the use of EN 397 compliant safety helmets to reduce the risk of head injuries in hazardous work environments.
7. Compatibility
EN 397 is compatible with other European workplace safety standards, allowing for a comprehensive approach to employee protection. This compatibility ensures that various aspects of safety gear, such as eye protection, respiratory protection, and hearing protection, can work together effectively to enhance overall workplace safety.
In summary, EN 397 is a critical European standard that sets the requirements for industrial safety helmets used in a variety of work environments. Compliance with this standard helps mitigate the risk of head injuries and promotes a safer and healthier workplace in Europe. Users and employers should ensure that the headgear they use meets EN 397 standards to enhance safety and reduce the risk of accidents and injuries on the job.
GB 14866-2006 is a Chinese national standard that sets forth the specifications and requirements for safety glasses. Developed by the Standardization Administration of China (SAC), this standard is crucial for ensuring the safety of individuals who use protective eyewear in various industrial and occupational settings within China. Here’s an overview of GB 14866-2006:
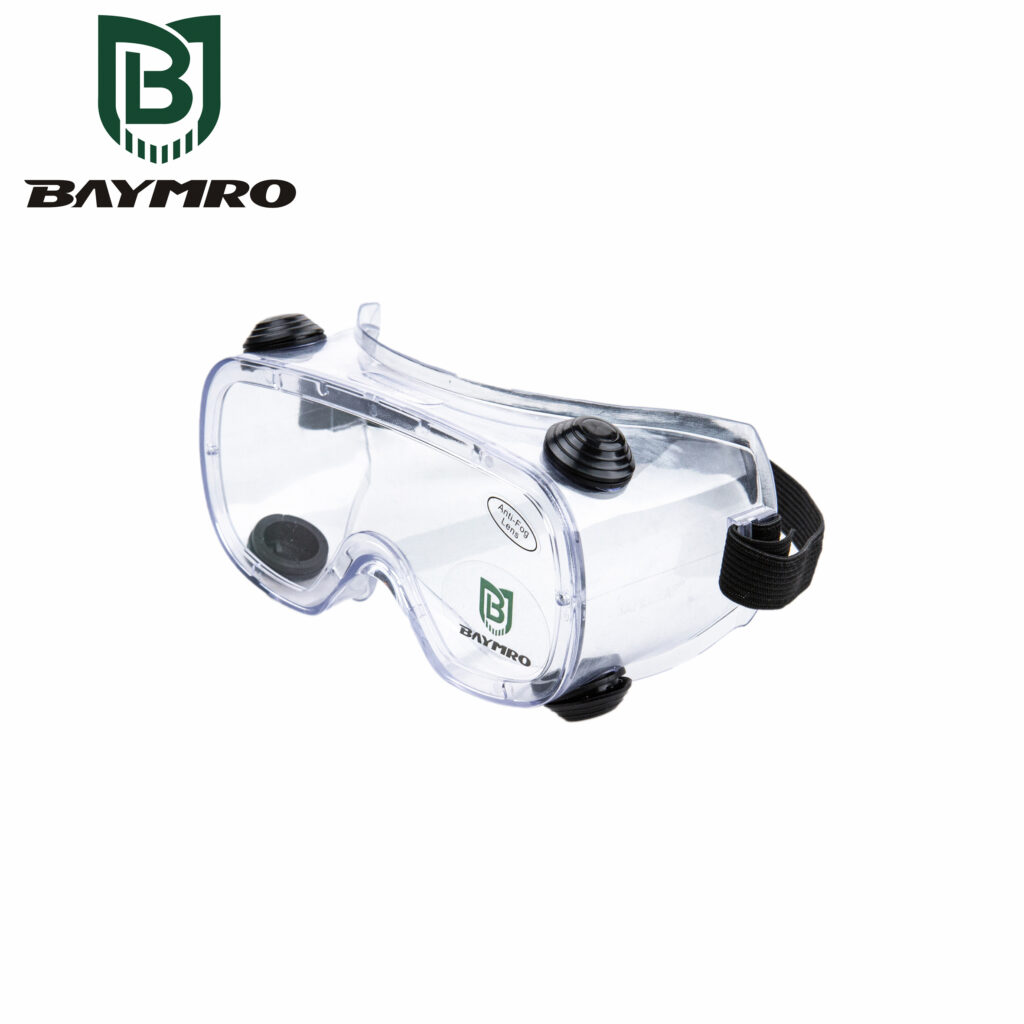

1. Purpose and Scope
GB 14866-2006 primarily focuses on safety glasses used to protect the eyes from various hazards, including mechanical impacts, chemical splashes, dust, and optical radiation. The standard aims to establish a consistent framework for the design, testing, and performance of these protective glasses.
2. Types of Protection
This standard covers a range of protective eyewear, including safety glasses, goggles, and face shields. These devices are designed to safeguard the eyes against different risks commonly encountered in industrial, construction, laboratory, and other work environments.
3. Design Requirements
GB 14866-2006 outlines design requirements for safety glasses, ensuring they provide comprehensive protection without compromising comfort and usability. These requirements encompass factors such as impact resistance, optical clarity, and frame construction.
4. Testing Procedures
Safety glasses that comply with GB 14866-2006 must undergo rigorous testing procedures to verify their compliance with the standard. These tests evaluate various aspects of performance, including impact resistance, optical quality, and resistance to environmental factors.
5. Marking and Labeling
Products that meet the GB 14866-2006 standard must be marked and labeled accordingly. These markings typically include information about the manufacturer, product model, and compliance with the standard. Such markings help users identify suitable eyewear for their specific needs.
6. Workplace Safety
Compliance with GB 14866-2006 is essential for maintaining workplace safety in China. Employers are often required to provide and enforce the use of GB-compliant protective eyewear to reduce the risk of eye injuries in hazardous work environments.
7. Compatibility
GB 14866-2006 is often compatible with other Chinese workplace safety standards, allowing for a comprehensive approach to employee protection. This compatibility ensures that various aspects of safety gear, such as head protection or respiratory protection, can work together effectively.
In summary, GB 14866-2006 is a crucial Chinese national standard that sets the requirements for safety glasses and protective eyewear used in a variety of work environments. Compliance with this standard helps mitigate the risk of eye injuries and promotes a safer and healthier workplace in China. Users and employers should ensure that the eyewear they use meets GB 14866-2006 standards to enhance safety and reduce the risk of accidents and injuries in the workplace.
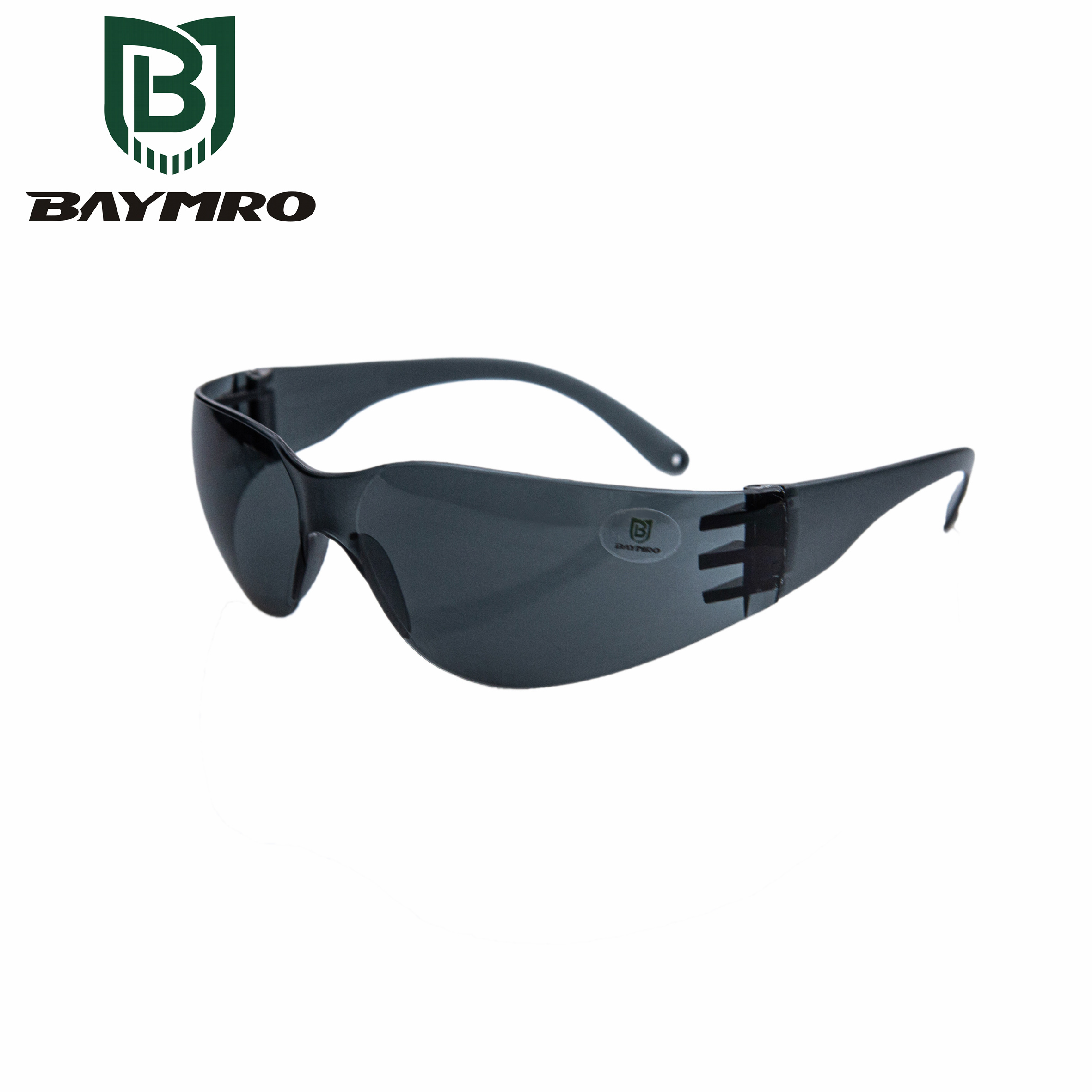
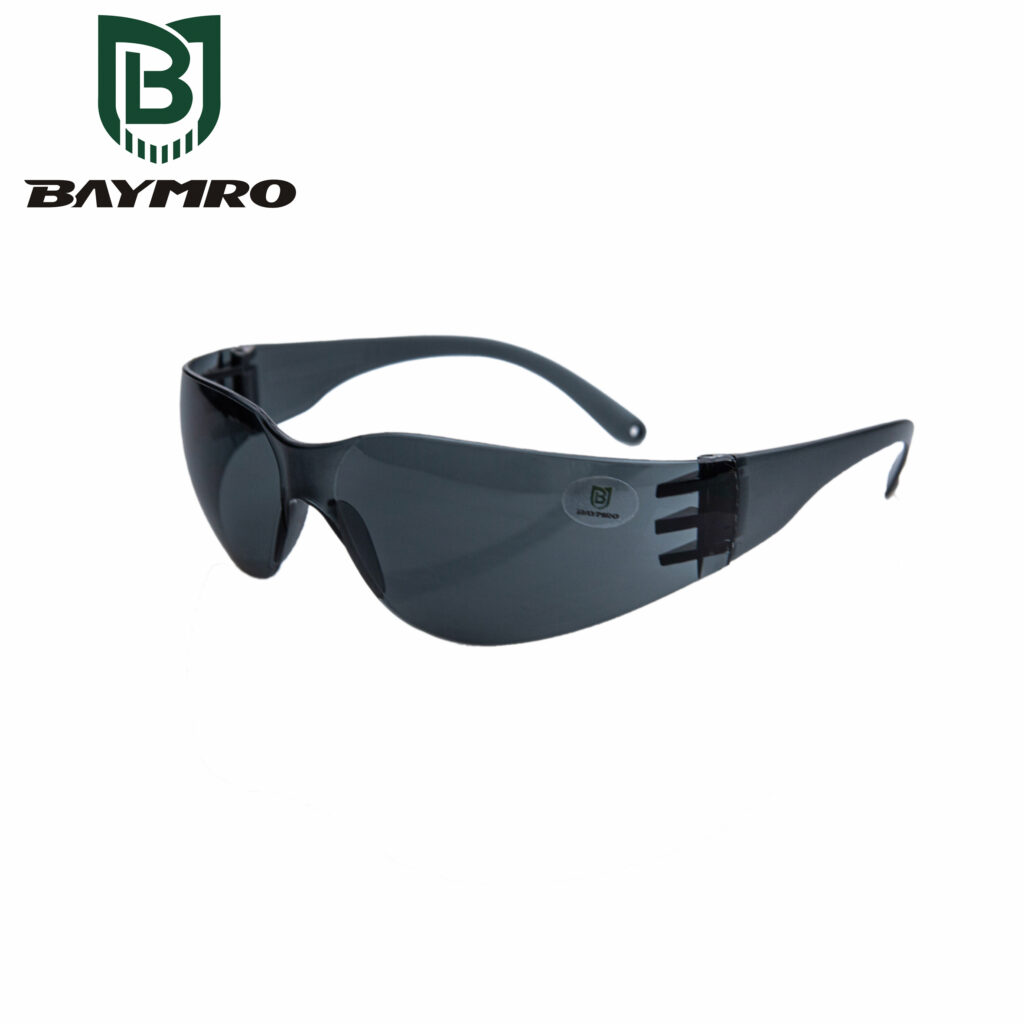


ANSI Z87.1 is an important standard developed by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) for the purpose of ensuring the safety and protection of industrial workers from various hazards that may affect the eyes and face. This standard specifically addresses eye and face protection products, such as safety glasses, goggles, face shields, welding helmets, and more. Let’s break down what ANSI Z87.1 signifies and its significance:
1. Purpose of ANSI Z87.1
ANSI Z87.1 serves as a comprehensive set of guidelines and requirements aimed at safeguarding the eyes and face of workers in industrial and occupational settings. The standard is designed to enhance workplace safety by establishing stringent criteria for the design, testing, and performance of protective eyewear and face shields.
2. Types of Protection Covered
ANSI Z87.1 covers a wide range of eye and face protection products, including:
Safety Glasses: Protective eyewear designed to shield the eyes from various hazards, including impact, chemicals, and UV radiation.
Goggles: Goggles provide a more comprehensive seal around the eyes, offering protection against splashes, dust, and chemical hazards.
Face Shields: These protective devices cover the entire face and offer additional protection against impact, chemical splashes, and other hazards. They are often used in conjunction with other eyewear.
Welding Helmets: Helmets designed for welding applications that provide protection against intense light, heat, and flying debris.
3. Design Requirements
The standard outlines design requirements for eye and face protection products. These requirements include specifications for impact resistance, optical clarity, and frame construction. Impact resistance ensures that the protective equipment can withstand a certain level of force without breaking or shattering, providing effective protection in the event of an impact.
4. Testing Requirements
ANSI Z87.1 includes rigorous testing requirements that products must undergo to demonstrate their compliance with the standard. These tests evaluate various aspects of performance, such as impact resistance, optical quality, and resistance to environmental factors.
5. Marking and Labeling
Products that meet the ANSI Z87.1 standard are required to be marked and labeled accordingly. These markings indicate the level of protection offered and provide essential information about the manufacturer and product compliance.
6. Workplace Safety
The adoption of ANSI Z87.1 compliant eye and face protection products in the workplace helps ensure the safety and well-being of industrial workers. It reduces the risk of eye injuries from mechanical, chemical, and other hazards, making it an essential component of workplace safety programs.
In summary, ANSI Z87.1 is a crucial American standard that sets the bar for the design, testing, and performance of eye and face protection equipment used in industrial and occupational settings. Compliance with this standard is essential for employers and individuals to ensure that protective eyewear and face shields effectively mitigate the risks associated with various workplace hazards, promoting a safer work environment.
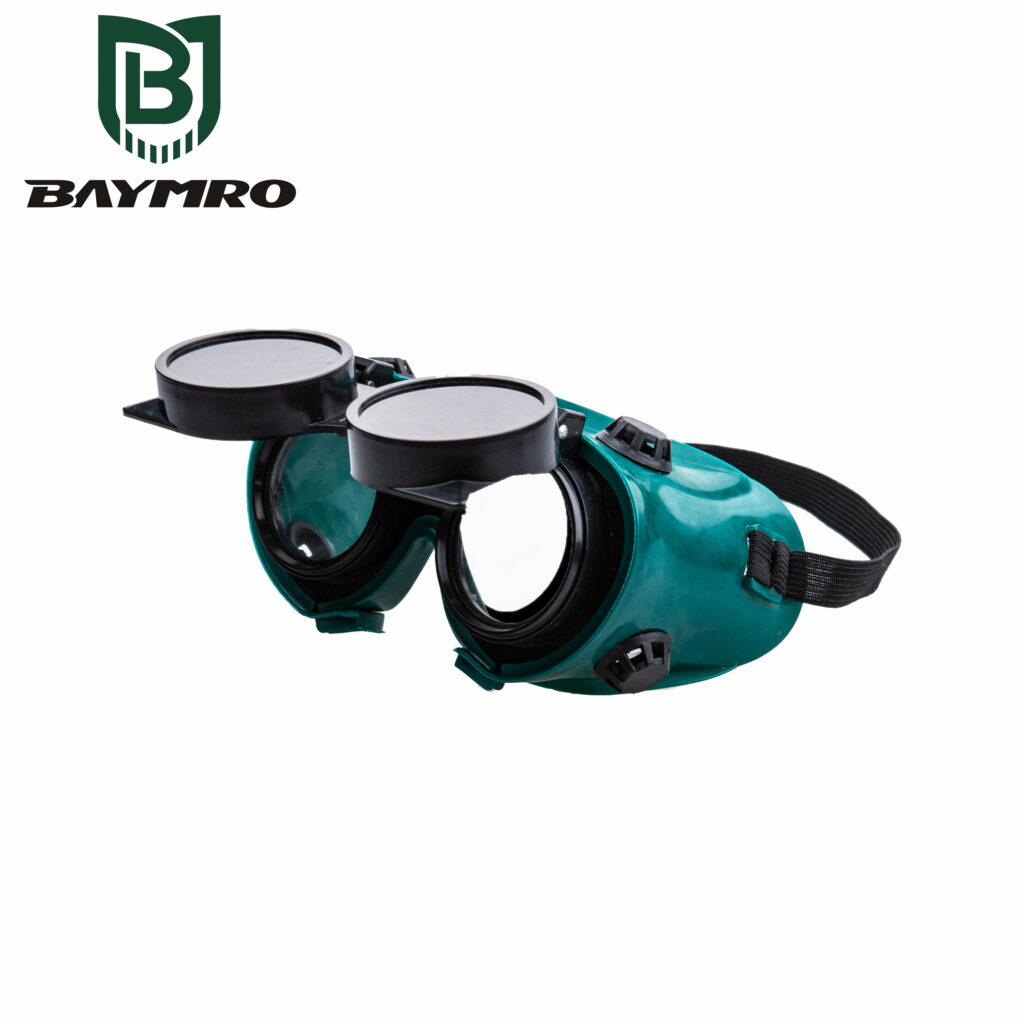

EN 169 is indeed an important European standard that pertains to personal eye protection, specifically focusing on filters designed for welding and related techniques. This standard ensures that eye protection equipment used in welding environments meets stringent requirements to safeguard the wearer’s eyes from the various hazards associated with welding processes.
Here’s a closer look at the key aspects of EN 169 and why it’s essential for ensuring safety in welding and similar high-risk environments:
1. Welding and Related Techniques
EN 169 primarily addresses eye protection for welding and related techniques. Welding generates intense light, heat, and sparks, making it a hazardous activity for the eyes. Therefore, specialized eye protection is crucial to prevent injuries caused by exposure to these welding-related hazards.
2. Flame and Hot Particle Resistance
One of the significant features of EN 169 compliant eye protection is its resistance to flames and hot particles. In welding environments, molten metal and sparks can pose a serious risk to the eyes. EN 169 compliant protective equipment is designed to withstand these conditions, reducing the likelihood of burns and injuries.
3. Hazardous Environment Suitability
EN 169 compliant eye protection is well-suited for the most hazardous welding environments, including industrial settings where arc welding, gas welding, and other welding techniques are commonly used. These environments often involve high temperatures, flying sparks, and the potential for exposure to harmful UV and infrared radiation, all of which require specialized protection.
4. Lens Filters and Shade Numbers
The standard specifies the performance requirements for lens filters used in welding eye protection. It also defines shade numbers that indicate the level of protection provided against the intense light generated during welding. The choice of shade number depends on the specific welding process and the intensity of the light produced.
5. User Comfort and Visibility
While safety is paramount, EN 169 compliant eye protection is also designed with user comfort and visibility in mind. Clear vision is crucial for welders to perform their tasks accurately. Therefore, these protective lenses are engineered to provide the necessary protection while ensuring that welders can see their work clearly.
6. Compliance Assurance
Manufacturers of eye protection equipment that adhere to EN 169 standards must undergo rigorous testing to ensure their products meet the specified requirements. Compliance with the standard offers users confidence in the quality and effectiveness of the protective equipment.
In conclusion, EN 169 is a critical European standard that sets the benchmark for personal eye protection in welding and related techniques. It ensures that eye protection equipment is resistant to flames and hot particles, making it ideal for use in the most hazardous welding environments. Compliance with EN 169 is essential for the safety and well-being of welders and workers exposed to similar high-risk conditions.

Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is a potent threat to our eyes, and prolonged exposure can lead to various eye conditions and even blindness. To safeguard against such risks, European Standard EN 170:2002 was developed. This standard sets forth the requirements and guidelines for ultraviolet filters used in personal eye protection. In this article, we’ll delve into the key aspects of EN 170:2002.

1. Purpose of EN 170:2002
EN 170:2002 primarily focuses on ultraviolet filters and their transmittance requirements. These filters are designed to protect the eyes from harmful UV radiation, which can originate from various sources, including the sun and certain industrial processes. The standard establishes standards for the performance of these filters and provides guidance on their use.
2. Transmittance Requirements
The standard specifies both scale numbers and transmittance requirements for ultraviolet filters. Transmittance refers to the amount of UV radiation that can pass through the filter. By setting clear requirements, EN 170 ensures that these filters provide effective protection against harmful UV rays.
3. Compatibility with EN 166
EN 166 is another European standard that addresses personal eye protection, covering a wide range of eye protection equipment. EN 170 complements EN 166 by focusing specifically on the requirements for ultraviolet filters. The frames and mountings to which these filters are affixed must comply with the applicable requirements in EN 166. This ensures that the complete eye protection apparatus is safe and reliable.
4. Selection and Use Guidance
Annex B of EN 170:2002 provides valuable guidance on the selection and use of ultraviolet filters. It assists users in choosing the right filter for their specific applications and highlights best practices for their proper utilization. This guidance enhances user safety and the effectiveness of the protective filters.
5. Limitations
It’s important to note that the protective filters discussed in EN 170 are not suitable for direct viewing of intense sources of bright light, such as Xenon high-pressure arc lamps. Additionally, they are not intended for direct or indirect observation of an electric welding arc. These situations require specialized eye protection equipment designed to handle extremely high-intensity light sources.
6. Marking and Numbering
EN 170 references the numbering table for filters and provides guidelines for marking oculars (lenses) and frames of eye protection equipment. Proper marking helps users identify the level of protection and ensures compliance with the standard.
In conclusion, EN 170:2002 is a vital European standard that addresses the protection of the eyes from harmful ultraviolet radiation. It sets out clear requirements for ultraviolet filters and offers guidance on their selection and use. By adhering to EN 170, individuals and employers can ensure that their eye protection equipment provides adequate defense against UV radiation, helping to safeguard eye health in various settings.

In a world where safety and protection are paramount, standards play a vital role in ensuring products meet stringent quality and performance standards. When it comes to protective gloves, one of the most frequently searched standards is EN ISO 374. This comprehensive guide aims to clarify key aspects of EN ISO 374, address common issues and clarify its importance in protecting hands from various hazards.
What is EN ISO 374?
EN ISO 374 is an important European standard that specifies the requirements for protective gloves designed to protect the wearer against hazardous chemicals and microorganisms. These gloves are widely used in industries where workers are exposed to hazardous substances such as chemicals, biological agents and viruses.
Why is EN ISO 374 important?
The importance of EN ISO 374 lies in its role in safeguarding the health and safety of workers. Exposure to hazardous chemicals and microorganisms can cause serious health problems ranging from skin irritations to life-threatening illnesses. Gloves complying with EN ISO 374 are rigorously tested to ensure they are effective against these risks.
What hazards does EN ISO 374 address?
EN ISO 374 mainly addresses two categories of hazards: chemical and microbiological. Chemical hazards cover a wide variety of substances, including acids, solvents, oils, and more. Microorganisms include bacteria, viruses and fungi, which are of particular concern in healthcare and laboratory settings.
How is EN ISO 374 testing performed?
Gloves are subjected to a battery of tests to assess their resistance to penetration, degradation and penetration. Penetration testing measures the time it takes for a chemical to penetrate the glove material, while degradation testing evaluates the physical changes to the glove after contact. Penetration testing evaluates a glove’s resistance to liquid and microbial intrusion.
What do the EN ISO 374 symbols mean?
EN ISO 374 Gloves are marked with a series of symbols indicating their performance against specific chemicals. These symbols consist of letters and numbers corresponding to the list of defined chemicals. Breakthrough times and penetration rates are indicated, providing the user with important information about the protective capabilities of the glove.
Are EN ISO 374 gloves reusable?
Whether a glove is reusable depends on its specific classification. Some EN ISO 374 gloves are designed for single use and must be disposed of after exposure to hazardous substances. Others are designed for multiple uses, and the manufacturer provides guidelines for proper decontamination and storage.
Is virus protection included in EN ISO 374?
Although EN ISO 374 was not originally designed with virus protection in mind, the standard’s test methods can be adapted to evaluate the barrier performance of gloves against viruses. However, it is worth noting that achieving virus protection requires specific testing for the relevant viruses, which may fall under different standards or certifications.
In summary:
EN ISO 374 is the cornerstone in the field of protective gloves, providing a standardized framework for evaluating the ability of gloves to protect against hazardous chemicals and microorganisms. The widespread interest in the standard is evidence of the growing awareness of workplace safety and the need for reliable protective equipment. By understanding the intricacies of EN ISO 374 and the information conveyed by its symbols, users can make informed decisions to ensure their safety and well-being in hazardous environments.
Introduce
In a world where safety is paramount, protective gear plays a vital role in protecting us from potential dangers. EN388 is a beacon of protection when it comes to choosing the right glove for tasks ranging from handling sharp objects to abrasive surfaces. In this article, we take a deep dive into EN388, demystify it, and provide insights so you can make an informed decision about protective gloves.
Uncovering EN388: Safety Language
Imagine if a glove could communicate its protective capabilities to you in a clear and concise manner. This is exactly what EN388 does. EN388 is more than just a standard; this code speaks volumes about the ability of gloves to protect hands from mechanical risks. By analyzing this code, you can unlock a wealth of information about the glove’s performance.
The Power of Numbers: Decoding EN388 Ratings
EN388 uses a numerical rating system to provide a comprehensive assessment of glove effectiveness in four key areas:
Abrasion Resistance (0-4): This number indicates how well the glove withstands abrasion. The higher the number, the greater the resistance.
Blade Cut Resistance (0-5): The second number evaluates the glove’s ability to resist sharp objects. Higher numbers indicate better cut resistance.
Tear Resistance (0-4): The number here emphasizes how durable the glove is against tearing forces. Higher numbers indicate increased tear resistance.
Puncture Resistance (0-4): This rating quantifies the glove’s ability to resist puncture by sharp objects. The higher the number, the better the puncture resistance.
EN388: Beyond numbers
EN388 doesn’t just stop with numbers; it extends its scope with symbols that provide supplementary information:
Impact Protection (P): The “P” symbol indicates that the glove provides additional impact protection, making it ideal for tasks involving striking objects.
Protection Against Rotating Machinery (T): When you spot the “T” symbol, it means the glove is designed to prevent cut hazards from rotating machinery.
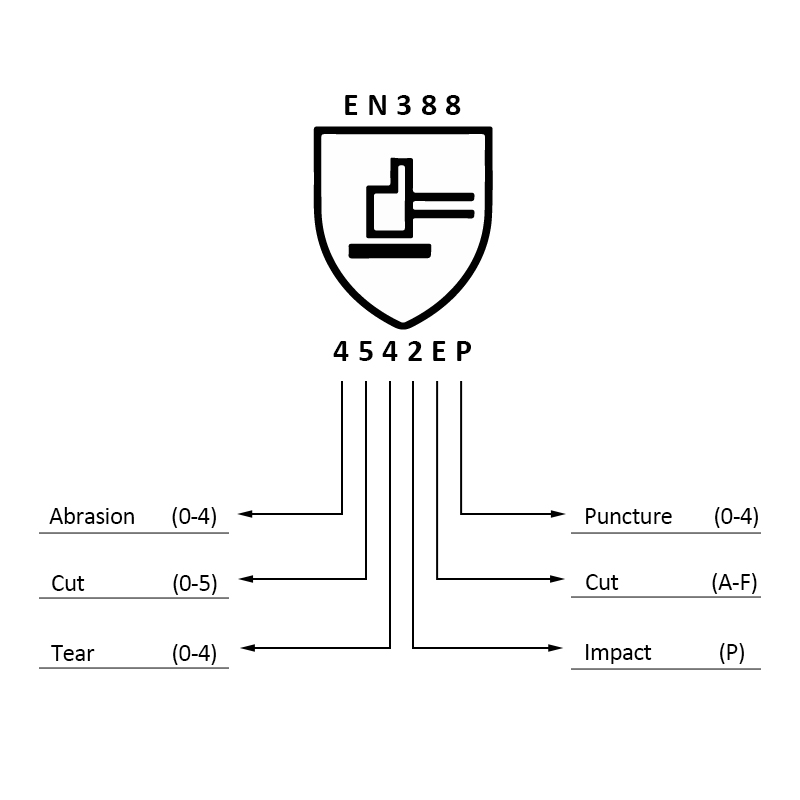
Interpreting EN388 marking
Imagine a glove marked “4542”. Let’s break down what this code reveals:
Abrasion resistance: level 4 (strong protection)
Blade Cut Resistance: 5 (Excellent Cut Protection)
Tear strength: Grade 4 (strong tear strength)
Puncture Resistance: 2 (good puncture protection)
Protection against rotating machinery: T (cut hazard)
Impact Protection: P (additional impact protection)
Why EN388 is your safety ally
EN388 translates complex technical details into a user-friendly format. It provides you with the knowledge to choose gloves that match the risks you face in your specific work environment. Whether you’re dealing with sharp blades, abrasive surfaces or machinery, EN388 guides your hands to optimal protection.
Conclusion: Improve Your Security Level
EN388 is more than a code; it’s your gateway to informed decisions. EN388, with its numerical rating and symbols, ensures you are not only wearing gloves, but wearing the correct gloves. Whether you’re a professional in a hazardous industry or a DIY enthusiast tackling household projects, EN388 can help you make an informed choice of gloves that provide custom protection.
From understanding its number system to embracing its symbols, EN388 enables you to elevate your safety levels. Don’t just wear gloves; embrace the language of safety with EN388 as your guide.
EN 17353:2020 standard supersedes two separate standards: EN 1150:1999 – ‘Protective clothing. Visibility clothing for non-professional use. Test methods and requirements’ – and EN 13356:2001 – ‘Visibility accessories for non-professional use. Test methods and requirements, both of which have now been withdrawn from use.
EN 17353 brings together elements of each of the withdrawn standards. However, all products meeting the requirements of the standard are no longer considered in terms of their use. Instead, their suitability in providing protection in medium risk situations is defined by their enhanced visibility properties.
The EN 17353 standard has also been devised to allow manufacturers more freedom in the design of products, given that enhanced visibility garments and devices are not intended for high-risk situations. Additionally, garments and devices are permitted for use in daylight (day) conditions only, dark (night) conditions only, or for both daylight and dark conditions.
 3M
3M Ansell
Ansell Dellta Plus
Dellta Plus Drager
Drager edelrid
edelrid Honeywell
Honeywell JUTEC
JUTEC lakeland
lakeland MSA
MSA New Pig
New Pig Weldas
Weldas